To achieve your goal of creating a reusable MyAutocomplete widget, you can define a custom stateful widget that encapsulates the Autocomplete logic and styling. Below is an example of how you can create a MyAutocomplete widget:
class MyAutocomplete extends StatefulWidget {
final List<String> options;
final String label;
final String hintText;
const MyAutocomplete({
super.key,
required this.options,
required this.label,
required this.hintText,
});
@override
State<MyAutocomplete> createState() => _MyAutocompleteState();
}
class _MyAutocompleteState extends State<MyAutocomplete> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Autocomplete<String>(
optionsBuilder: (TextEditingValue textEditingValue) {
if (textEditingValue.text == '') {
return const Iterable<String>.empty();
}
return widget.options.where((String option) {
return option.contains(textEditingValue.text.toLowerCase());
});
},
fieldViewBuilder: (BuildContext context, TextEditingController textEditingController, FocusNode focusNode, VoidCallback onFieldSubmitted) {
return TextFormField(
controller: textEditingController,
decoration: InputDecoration(
labelText: widget.label,
hintText: widget.hintText,
),
focusNode: focusNode,
onFieldSubmitted: (String value) {
onFieldSubmitted();
print('You just typed a new entry $value');
},
);
},
onSelected: (String selection) {
print('You just selected $selection');
},
);
}
}
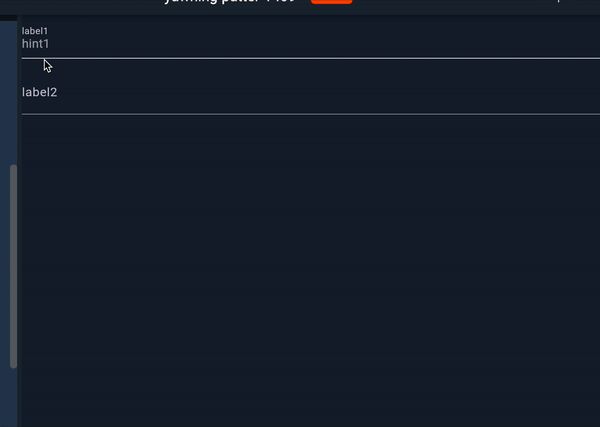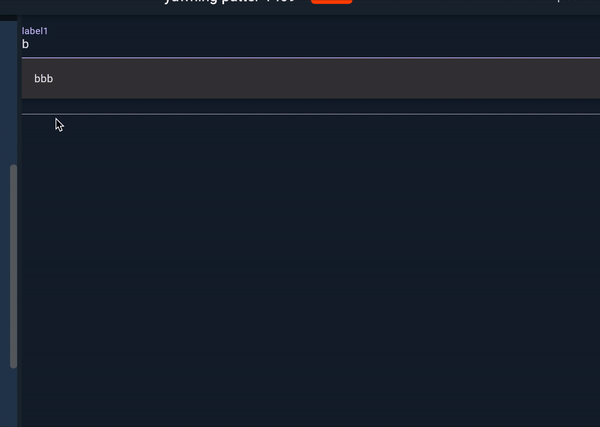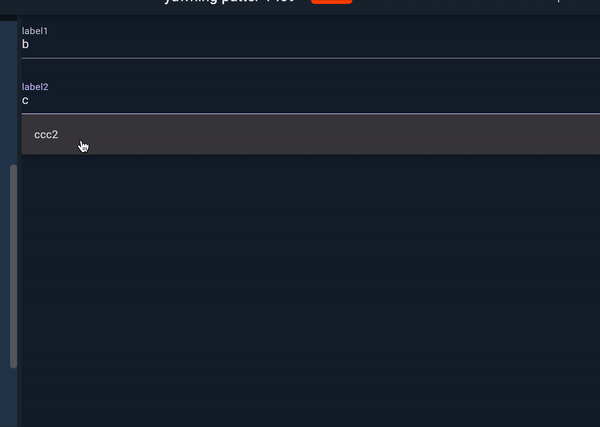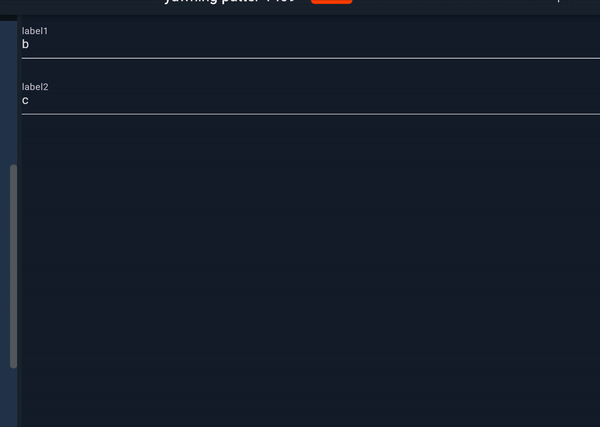
Now we can use reusable code as below:
class MyWidget extends StatelessWidget {
final List<String> list1 = ['aaa', 'bbb', 'ccc', 'aa1', 'aa2'];
final String label1 = 'label1';
final String hint1 = 'hint1';
final List<String> list2 = ['aaa2', 'bbb2', 'ccc2'];
final String label2 = 'label2';
final String hint2 = 'hint2';
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Column(
children: [
MyAutocomplete(options: list1, label: label1, hintText: hint1),
const SizedBox(height: 16.0),
MyAutocomplete(options: list2, label: label2, hintText: hint2),
// Add more MyAutocomplete fields as needed
],
);
}
}
Output: