It all started with the first textual content displayed on digital screens. The perception of human beings is not limited to the vision only but hearing, touching, smelling and tasting too. We have enabled countless books’ textual content accessible by braille but what about digital devices. Nevertheless, in electronic devices, the ability of hearing and audio technologies have been helping us.
Electronic Devices do not only display visual content but, comes with listening and speaking ability.
“Till the time, websites were building to sell the products as well as services considering the target audience only, but in today’s digital edge, things have entirely transformed.“
Web Accessibility is all about building websites and tools that can be accessible in a plethora of ways, hence the people with diverse disabilities can access it in one or another way.
In the 21st-century world, numerous countries have taken solid steps towards making all content graspable in every possible format. For instance, the government of Ontario state in Canada has formed the standard and an act named AODA – Accessibility for Ontarians with Disabilities Act. They have set rules under AODA standards for various sectors of the economy, Web Standards have been found a crucial fragment of it.
Moreover, In the US, Section 508 – Rehabilitation Act Amendments of 1998 states, “Electronic and information technology must be equally accessible to people with and without disabilities”.
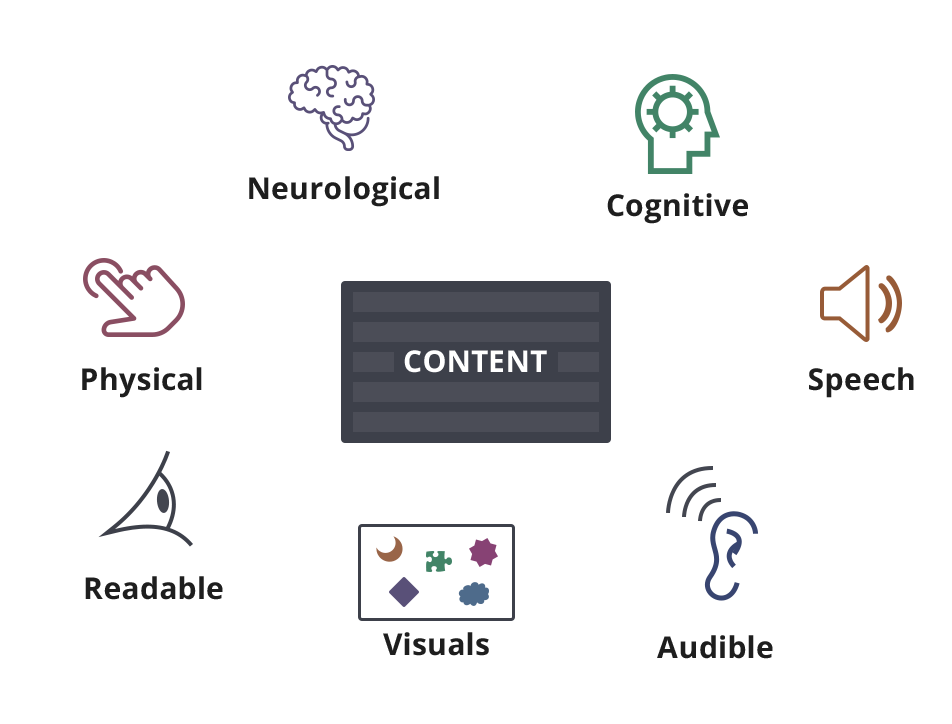
Here is a rundown of content absorbed by humans in multiple ways.
For Web Accessibility, AODA recommends WCAG – AA ( Web Content Accessibility Guidelines ). WCAG has defined three levels of conformance, where
A – the lowest, AA, and AAA – the highest.
Here are a few ways to implement Web Accessibility on a website.
1. Navigation
Navigation is the core chunk of any website. Manage proper order of focus, keyboard shortcuts ( Tab and Shift + Tab ) play a vital role here. Ensure essential keyboard keys are working.
2. Colors

Provide adequate contrast with the help of background color and text color. Avoid low contrast design. Light background with dark content or vice versa works finer concurrently.
3. Titles and Headings
Proper usage of headings and titles in hierarchy creates a difference. One h1 tag per page shows the main heading of the page. Then, in order h2, h3 and upcoming lower sized headings. Relevant terminology, compact and well described titles are eloquent for any type of user.
4. Semantic Structure
Have a purpose for everything that can be defined. Like never write < ol > or < ul > for indentation. < ol > tag for sequence and < ul > for unordered list. < strong > should be preferred instead of bold showing the importance of the word.
5. Hyperlinks
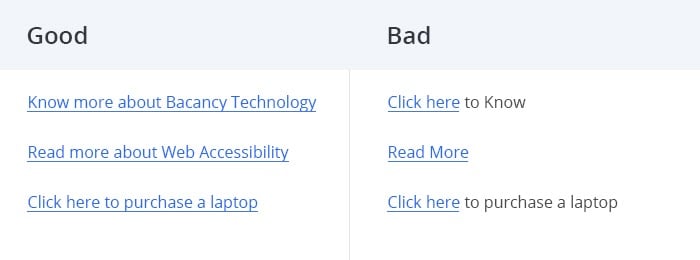
Links with relevant descriptions stirs the pot. Kindly avoid general names like “click here”, “download” and “go to”. Instead apply terminology such as “Reset Password”, “Download Video” and “Profile”.
6. Images
There are a plethora of images in websites that can be described by the “alt” attribute. For instance, If there is a logo it should be described as the brand name or with purpose therefore the user who is not disable can also know what it stands for.
7. Provide accessible documents
Word, Power-Point, Excel, HTML, PDF etc.
8. Accessible Multimedia
Provide Audio, Video or, Audio-Video formats of textual content. Media players must be controlled by keyboard.
Apart from the above points, implementation of clear language can be a good point to consider. Well defined content can never create a dilemma in a person’s mind.
Here we designers’ team at Bacancy Technology, walk with an agenda in mind to create a phenomenal website which works exceptionally well for every user. Wikipedia is not just great and infamous for its content but the availability and accessibility of its information in every possible format.
Hire Certified Web Accessibility Specialist
At Bacancy Technology, we have certified web accessibility expert, who have top-of-the-line expertise in creating a phenomenal website that works exceptionally well for every type of user.

Web Accessibility leads to finer User Experience for disable users, normal users and naive users too. Not in every situation, website users will be sitting in front of a desktop in ideal condition. The visitor may be using your product while driving a car, listening to music, roaming in a garden or working in an office.
By taking every scenario in consideration, one should shoot for the maximum. Providing great care to all types of visitors increases brand value by winning the trust of people.
Thus, never miss a single chance to convert your web content into more than one accessible format. There should be a long term vision and an altruistic intention behind enabling people with disabilities to work in every possible sector so the talent and full potential can be utilized that can help grow the nation.

