How to Create Web API using Entity Framework Core in .NET 6?
Last Updated on December 29, 2023
Quick Summary:
This tutorial covers the process of creating Web API using Entity Framework Core in .NET 6. You will learn how to develop a RESTful API by leveraging Entity Framework Core’s capabilities and implementing Repository Pattern.
ASP.NET core is a robust cross-platform framework for creating web applications and APIs. With the latest version, ASP.NET Core 6, you can easily leverage new features and enhancements to create high-performance and scalable APIs.
Here we will use Entity Framework Core, a widely popular Object -Relational Mapping (ORM) framework, to simplify the process of interacting with the database and provides an abstraction layer over the underlying data storage, making it easier to work with data.
We will also implement the Repository pattern, a widely used design pattern in software development. It provides a way to centralize data access logic and abstracts away the specific data access technology, making our code more modular and testable.
By the end of this tutorial, you will learn how to create Web API in ASP.NET Core 6 and implement repository pattern with Entity framework Core in .NET 6. So let’s get started!
Web API (Application Programming Interface) is a concept that operates on the HTTP Protocol, allowing applications to extend their functionality. It consists of a collection of functions that can be accessed by a broad range of clients, such as browsers, mobiles, iPhones, and tablets, via HTTP calls.
Web APIs can be developed using architecture patterns, including REST, SOAP, and RPC.
We will focus on creating a RESTful API following the REST pattern.
REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style for building web services. It utilizes HTTP methods such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE to perform CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations on resources. REST emphasizes using URIs (Uniform Resource Identifiers) to identify resources uniquely and enables clients to discover and interact with those resources through hypermedia. Web API created using this design pattern or architectural style is called RESTful API.
HTTP methods
Our tutorial will focus on using the GET and POST methods. But it is important to note that additional HTTP methods like PATCH, HEAD, and OPTIONS are available.
? Visual Studio 2022
? .NET 6 SDK
? SQL Server
Open visual studio 2022, create a new project, select ASP.NET Core Web API from templates, and click Next.
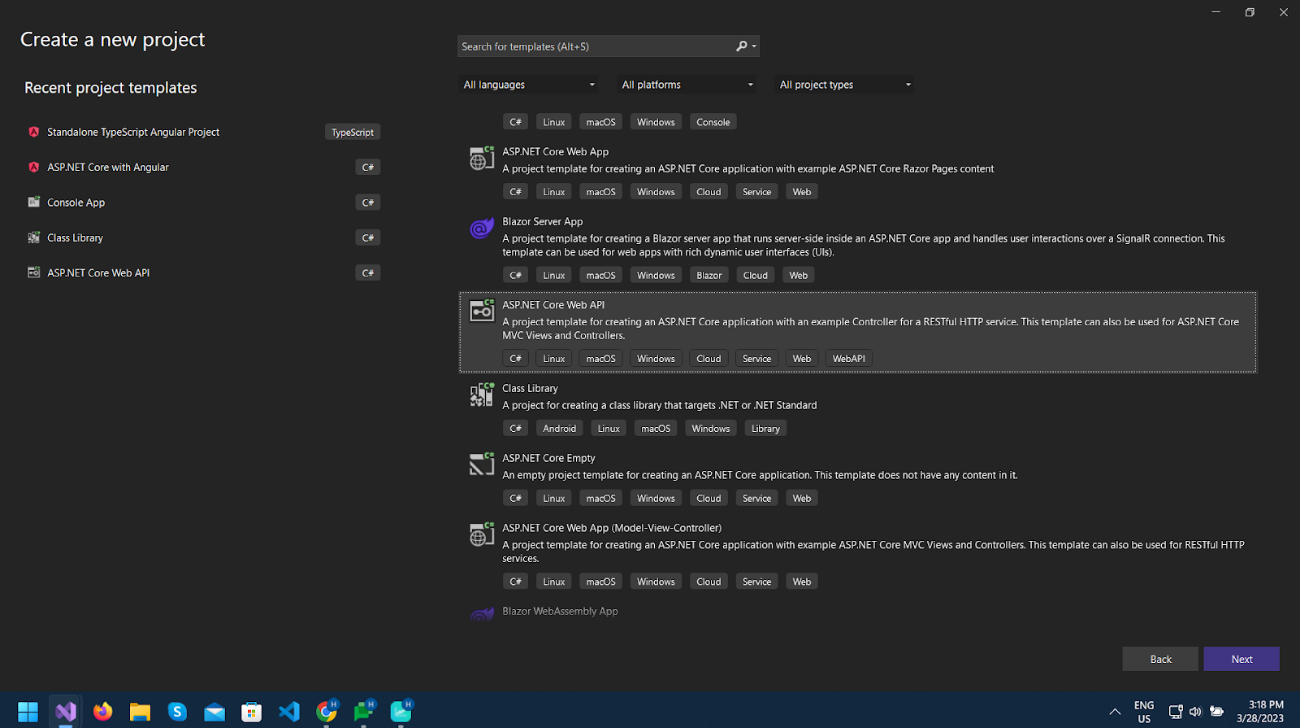
Give the project a name as you like and click Next.
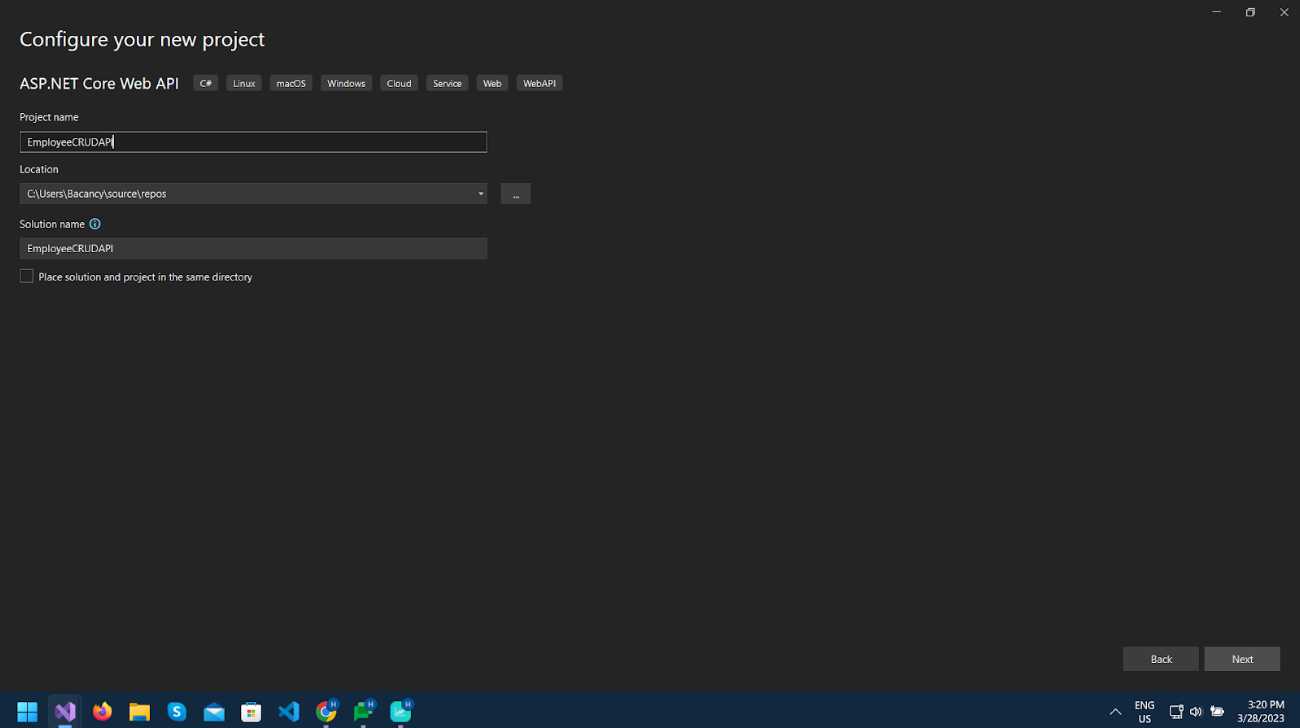
Select .NET 6 (Long Term Support) as Framework and click Next.
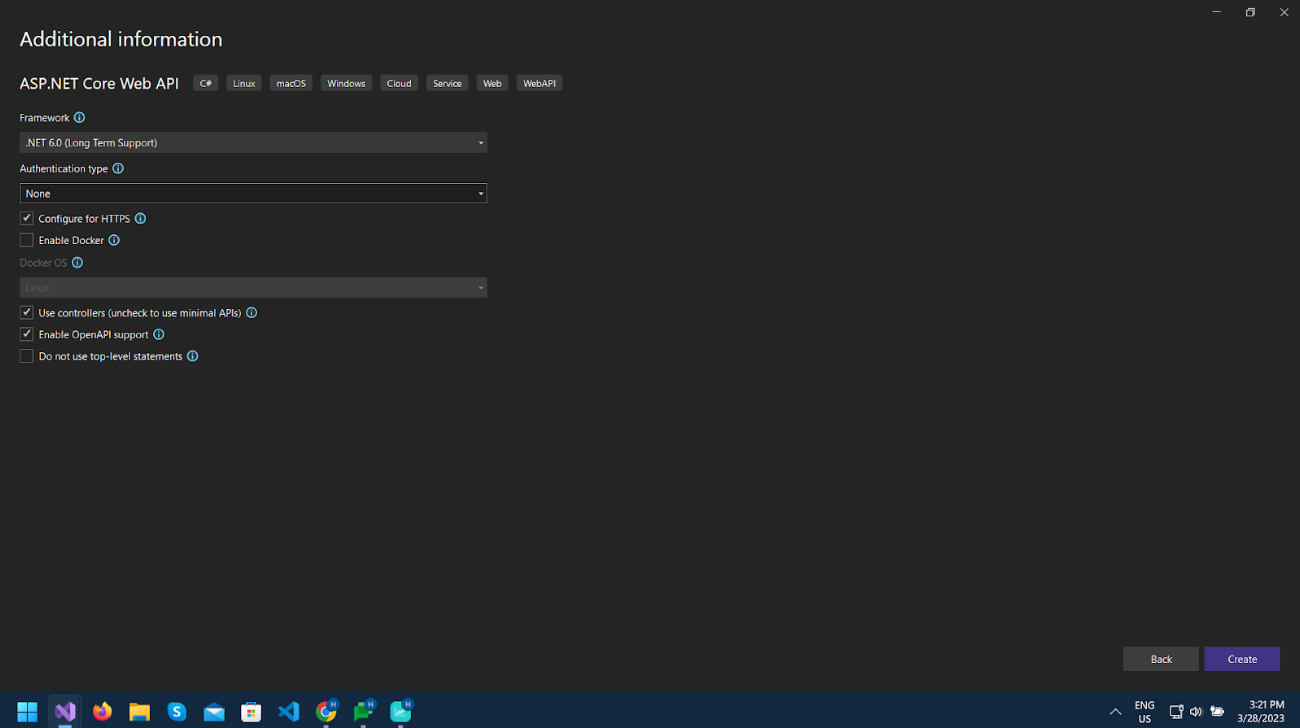
That will create a basic project with WeatherController class and also swagger support will be added automatically, which provides UI to interact with API in the browser.
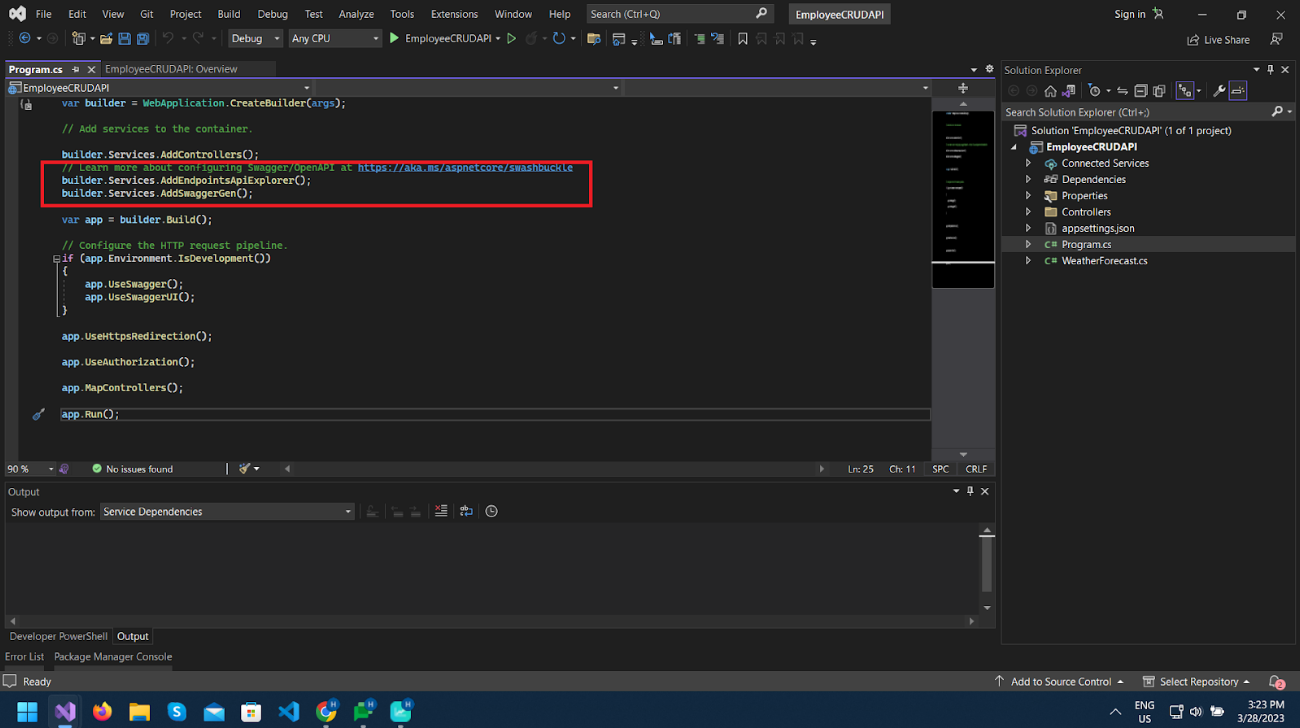
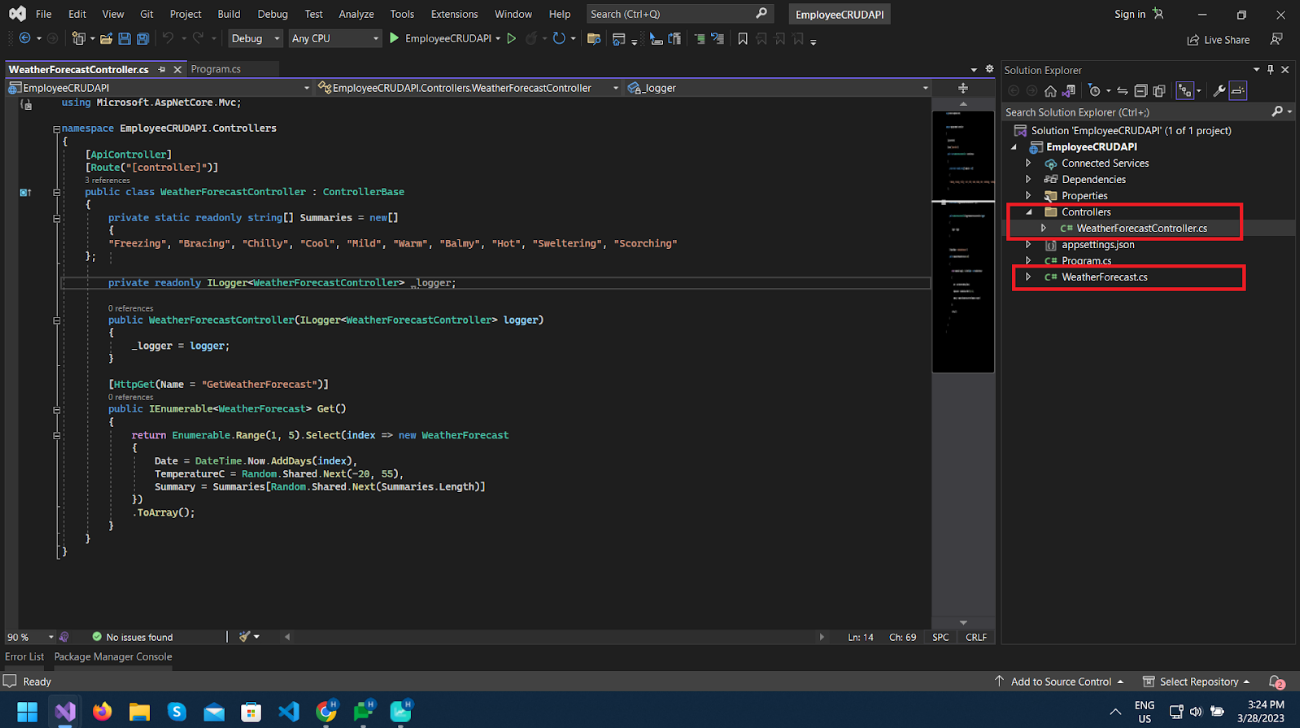
Now let’s run the project and see what happens.
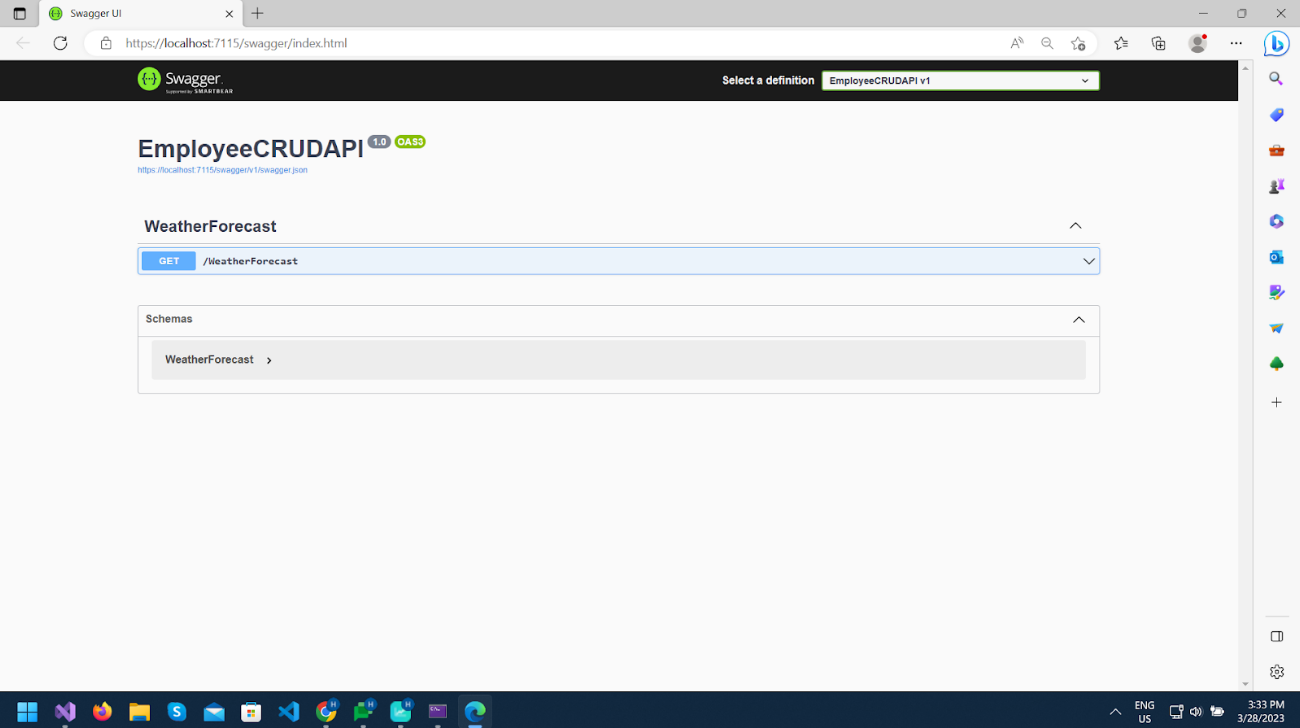
As you can see, the WeatherForecast GET method is displayed in the UI implemented in the WeatherForecast Controller.
Now execute this method.
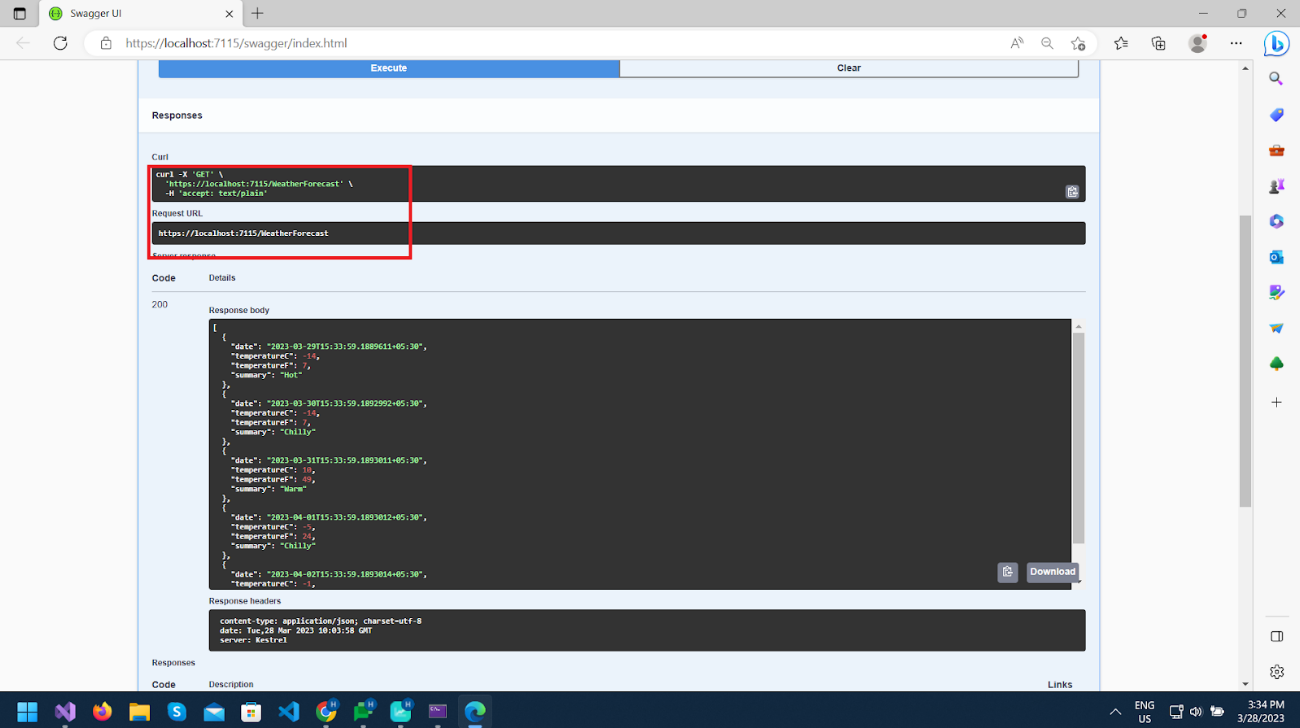
The controller provides a response on the specified URL, which can be accessed in a browser to verify the output.
We will create our new controller, model and add data in the database individually.
Let’s start by creating a Model.
Ready to level up your software development game?
Don’t miss out on the opportunity to hire dot net core developer who will revolutionize your software development process. Contact us today to get started!
Right-click on the project in Solution Explorer and Add > New Folder. Name it Models, where we will add our models and DbContext class that we will discuss later.
Now create a class in the Models folder and name it Employee.cs.
And create properties in it, as shown in the screenshot below.
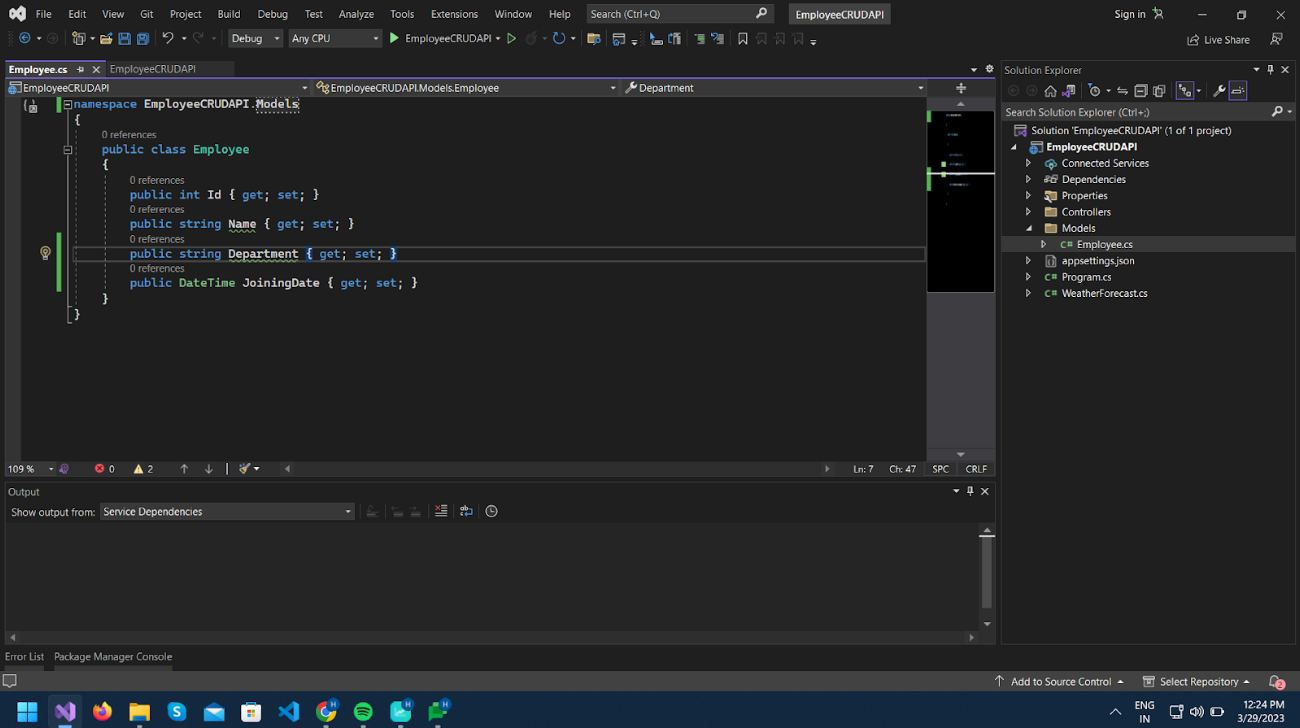
Now we will use Entity Framework Core to work with the database and generate our database tables using Code First from our Model classes.
Entity Framework(EF) is an object-relational mapper (O/RM) that enables .NET developers to work with a database using .NET objects. It eliminates the need for most of the data-access code that developers usually need to write.
We will use Entity Framework Core in .NET 6, a lightweight, extensible, open-source, and cross-platform version of Entity Framework data access technology. We can choose Database First or Code First approach for development with EF Core.
?Database First
In the Database First approach, we create Tables in the database first, and then we can generate entities using the Scaffold-DbContext command. It is preferred when the database schema already exists.
? Code First
In Code First, we will create models/classes of entities in our application, and using migrations and update database command, EF Core API will create/update the database as per entities defined in our domain application. It is used in applications that are highly Domain-Driver.
We will adopt the Code First approach since we do not have an existing database. We will create the database based on our classes and their relationships.
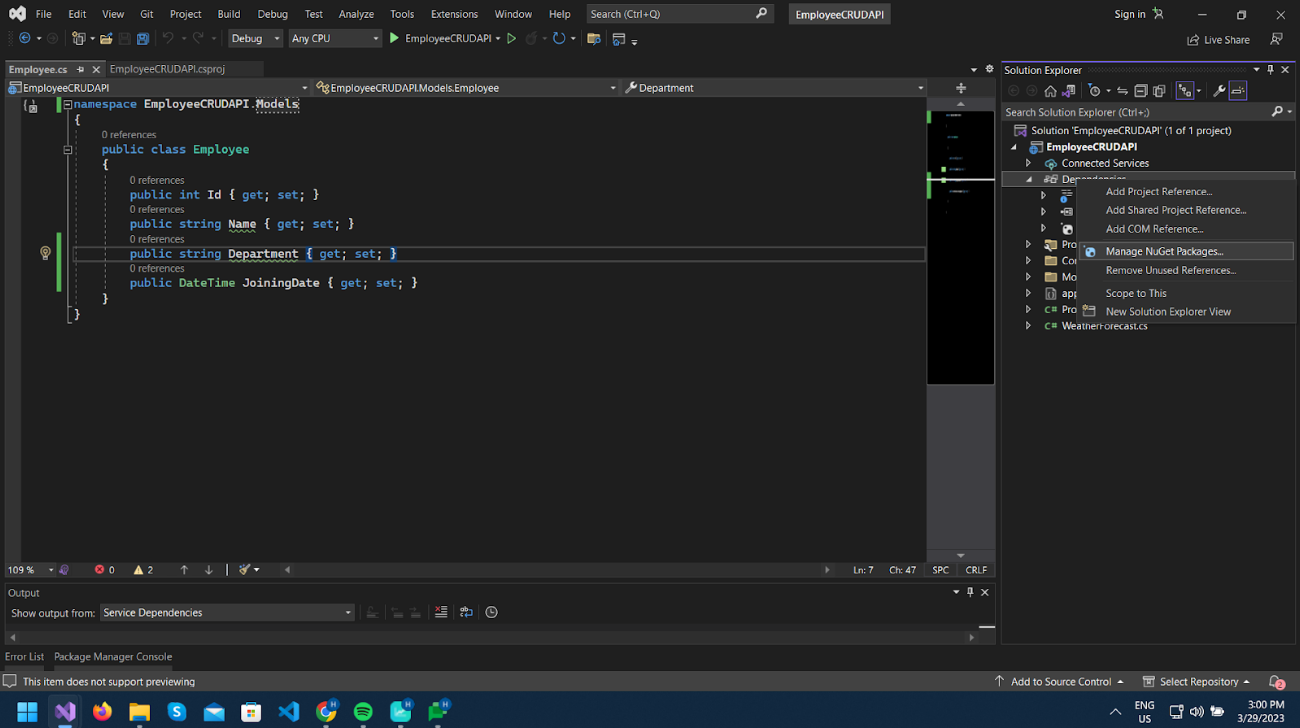
First, start by adding some required NuGet packages from Nuget Package Manager.
Right-click on the Dependencies, select Manage NuGet Packages and install the below Packages.
Microsot.EntityFrameworkCore
Microsot.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
Microsot.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools
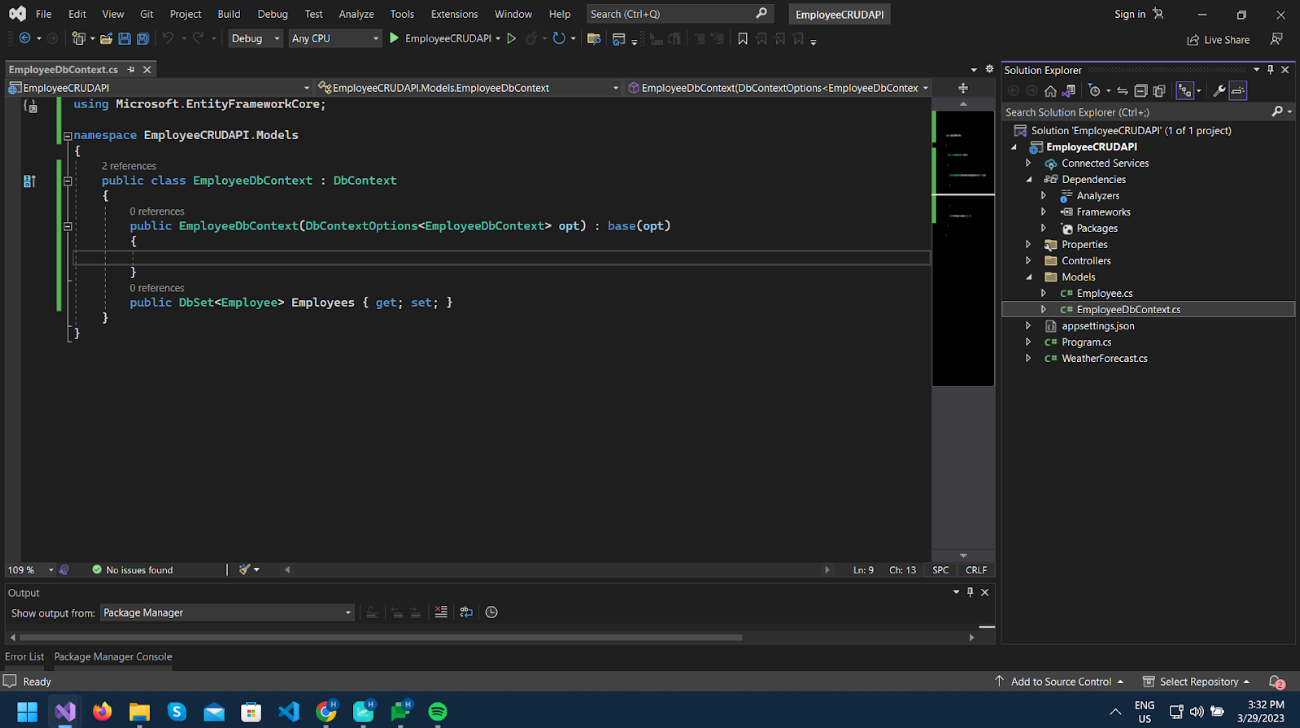
We will add a context class named EmployeeDbContext.cs in the Models folder, which should be derived from the DbContext class. This class will contain all the model’s information for creating the database tables.
We will add a DbSet property of type our Employee model.
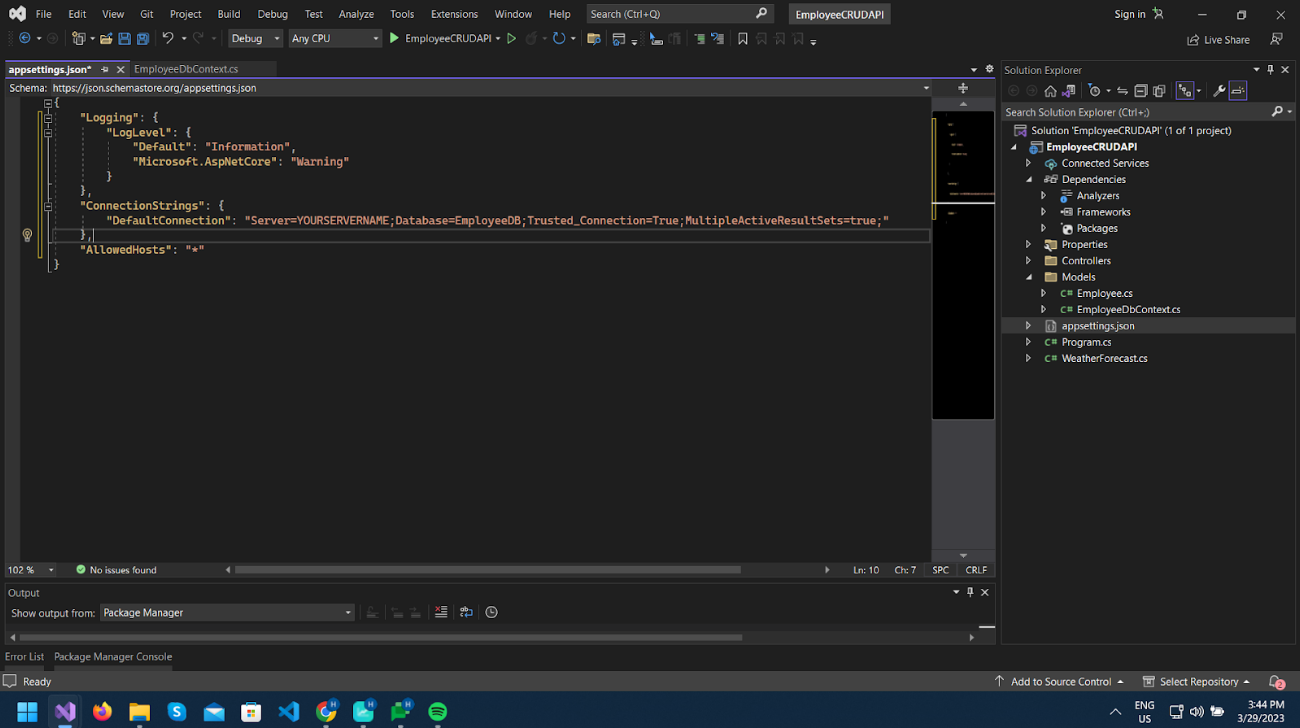
Now we will add the Connecting String for our database in appsettings.json.
Now register our EmployeeDbContext service as per below.
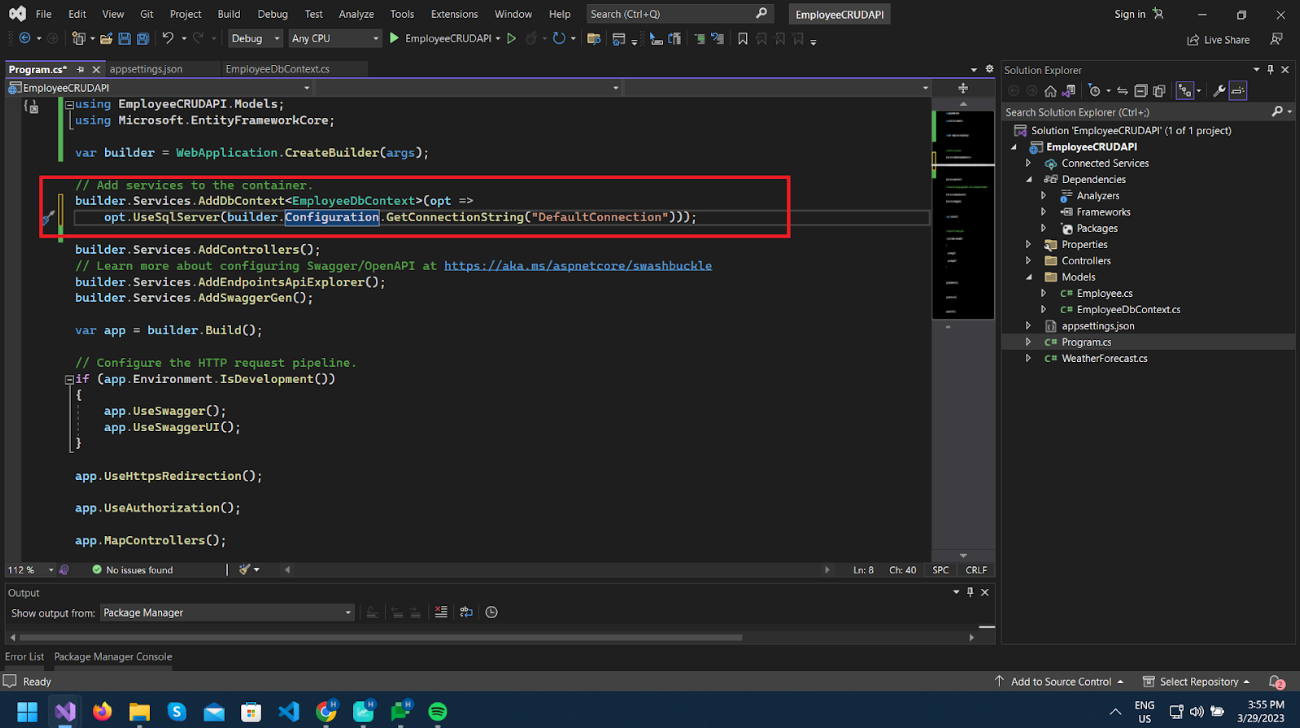
Now we will generate database schemas defined as per EmployeeDbContext.cs class using the Add-Migration command.
Open Tools > NuGet Package Manager > Nuget Package Console.
And write this command Add-Migration MIGRATION_NAME.
This command will add the Migration folder as per the below image, in which there will be a class name with datetime and name of migration. Here we have named the migration as InitialMigration.
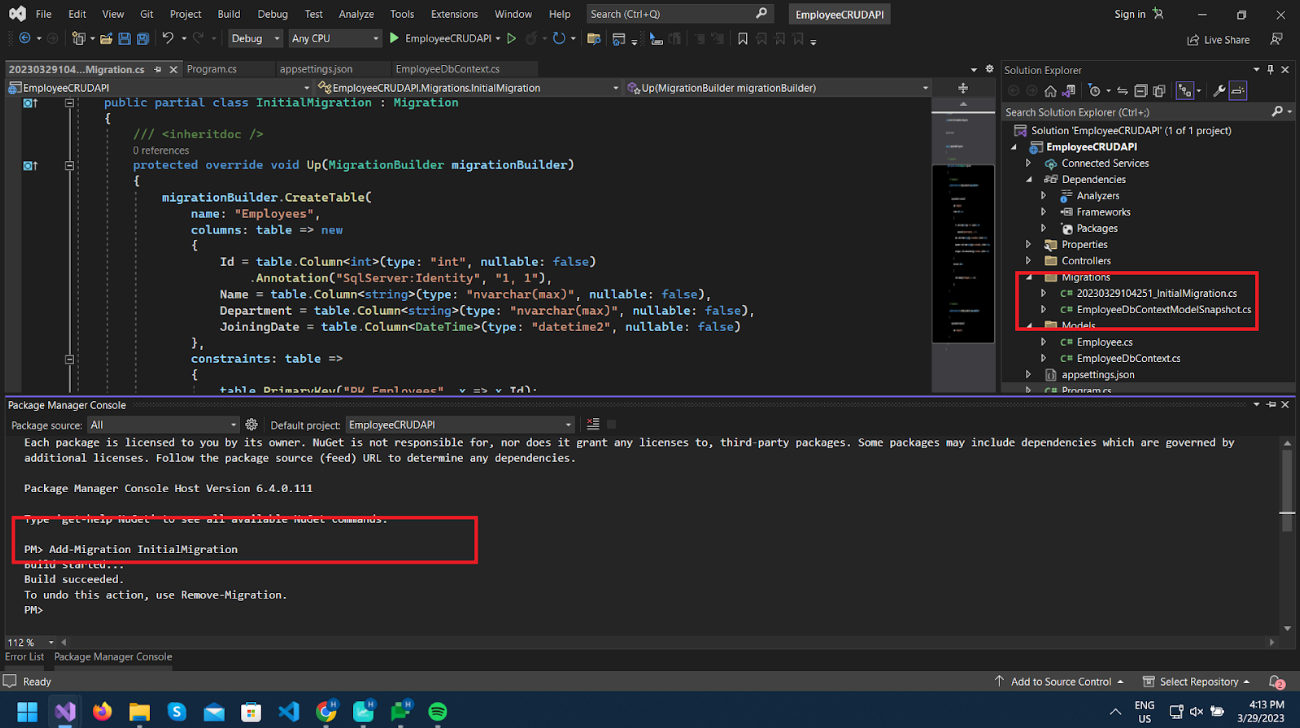
As you can see, the Up() method has some code for creating a Table as per EmployeeDbContext.cs class.
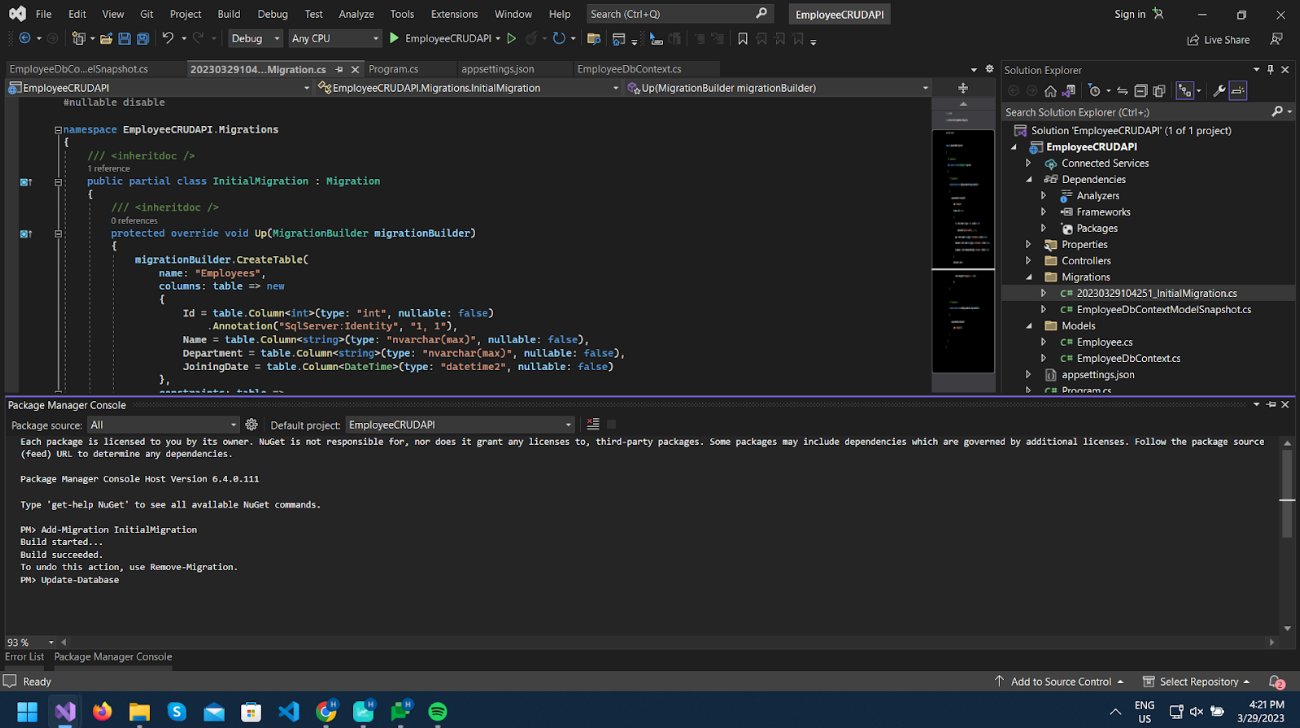
Now we will use Update-Database in Package Manager Console, which will execute code in the Up() method and create/update database schema according to it.
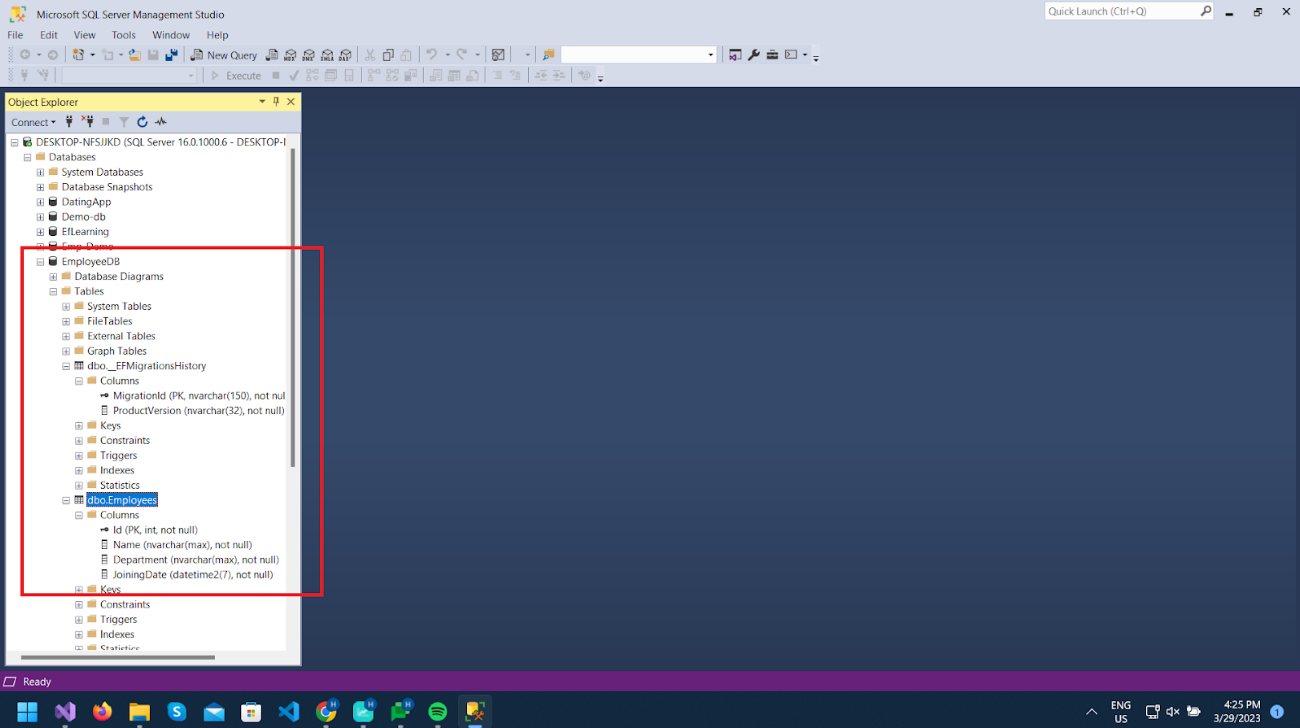
After completing that command, we can verify in our database that the database has been successfully created along with the addition of the Employee table. Also, a migration history table is created, which will have records of executed migration history.
Right-click on Controllers Folder, add a new API Controller, and name it EmployeesController.cs as per the image below.
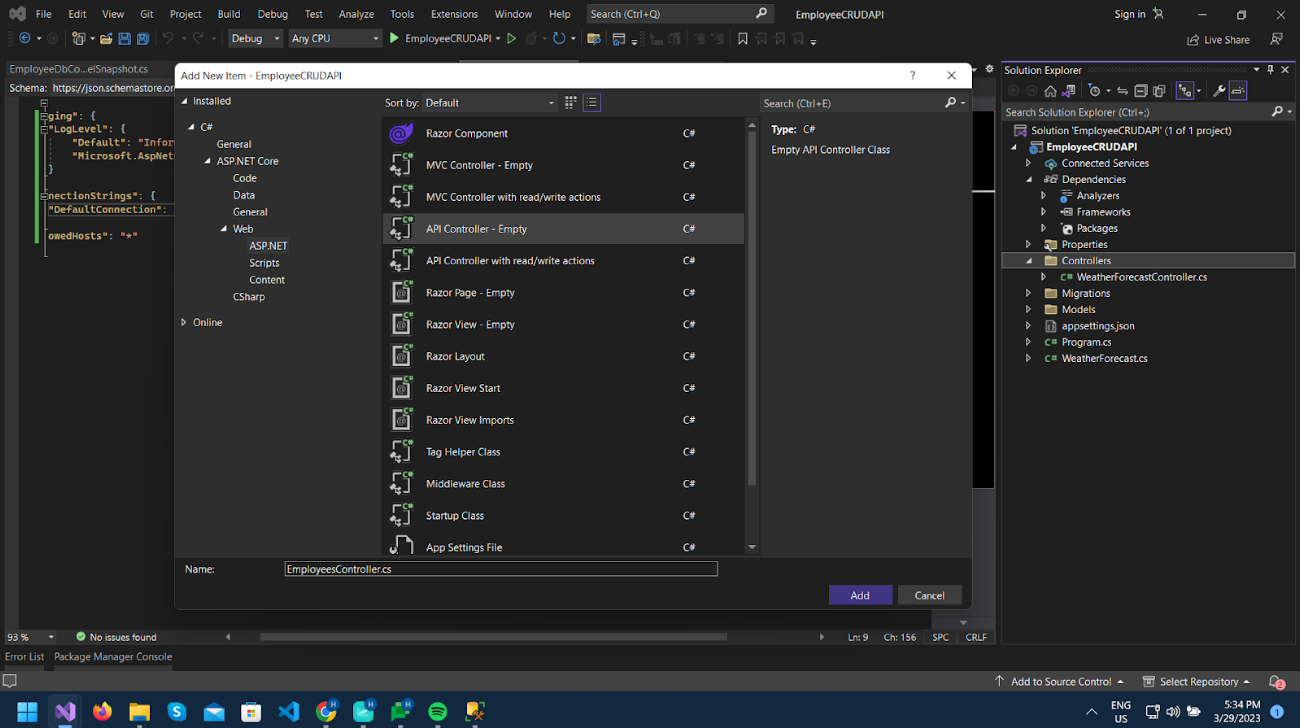
As you can see, the controller class is marked with the [ApiController] attribute. This attribute indicates that the controller responds to web API requests.
Route attribute defines the route for calling this controller.

Now we will create API to perform CRUD operation as below:
1. GET /api/Employees
2. GET /api/Employees/{id}
3. POST /api/Employees
4. PUT /api/Employees/{id}
5. DELETE /api/Employees/{id}
First, inject database context dependency through the controller to access EmployeeDbConext.
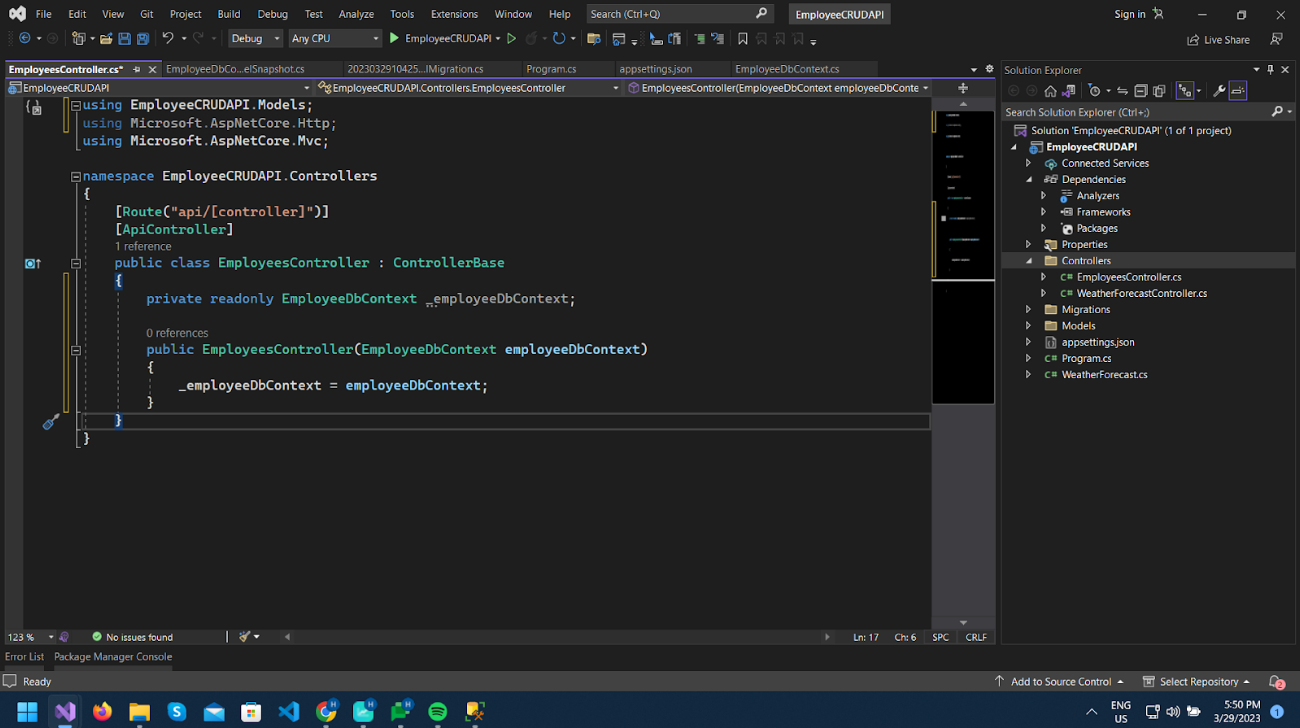
Now create two methods as per the below image.
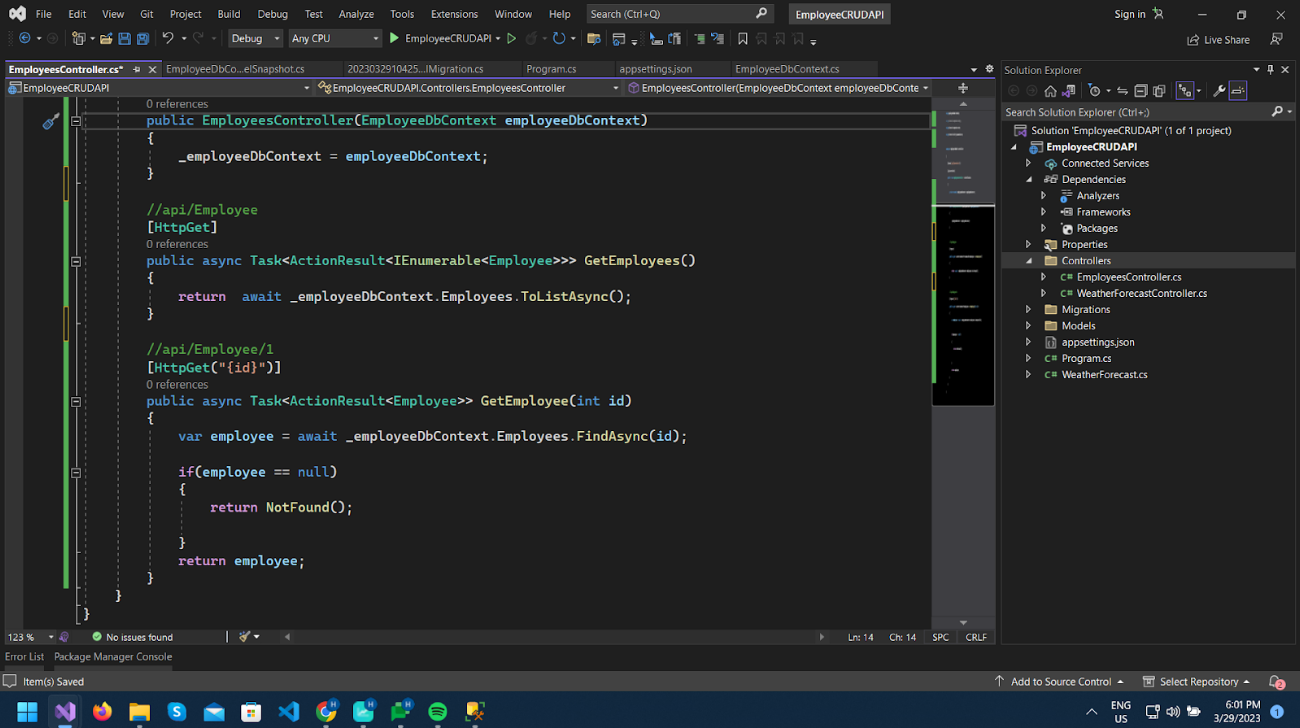
Let’s add data to the employee table and test it.
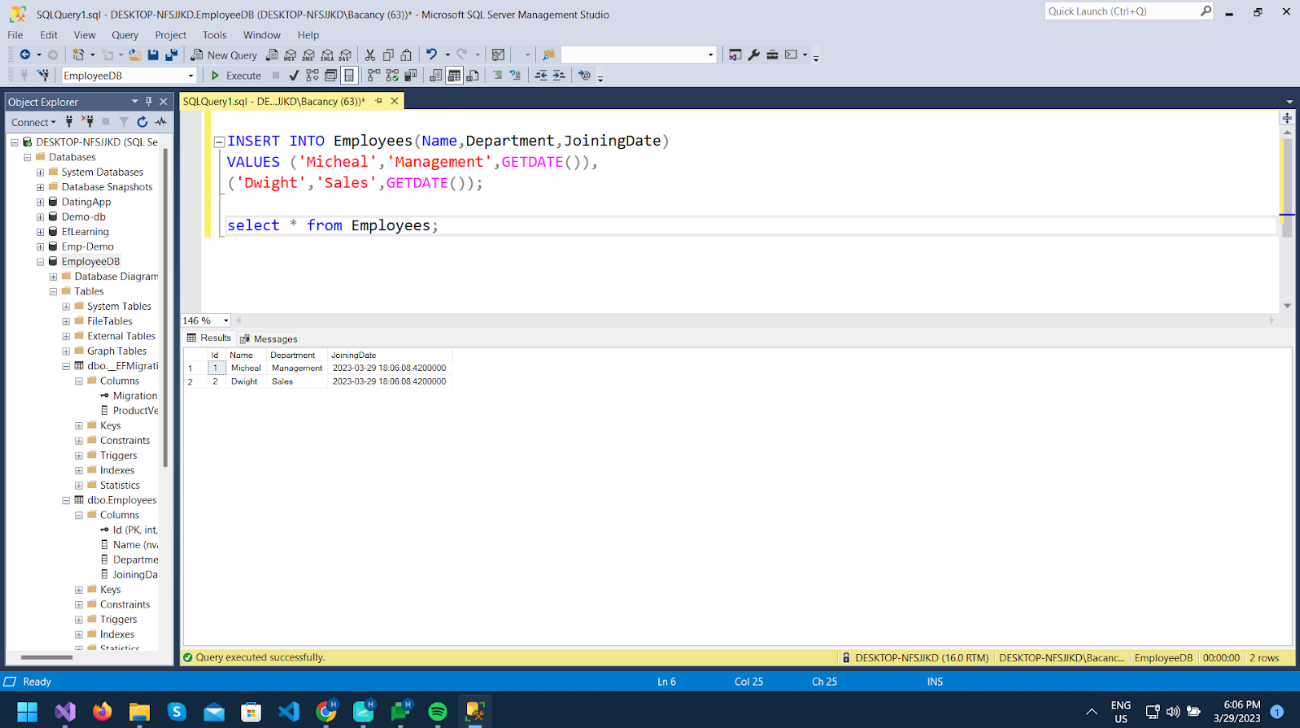
Now Run the project and test using Swagger.
As you can see, two new methods are showing in the UI. Let’s test both and check the result.
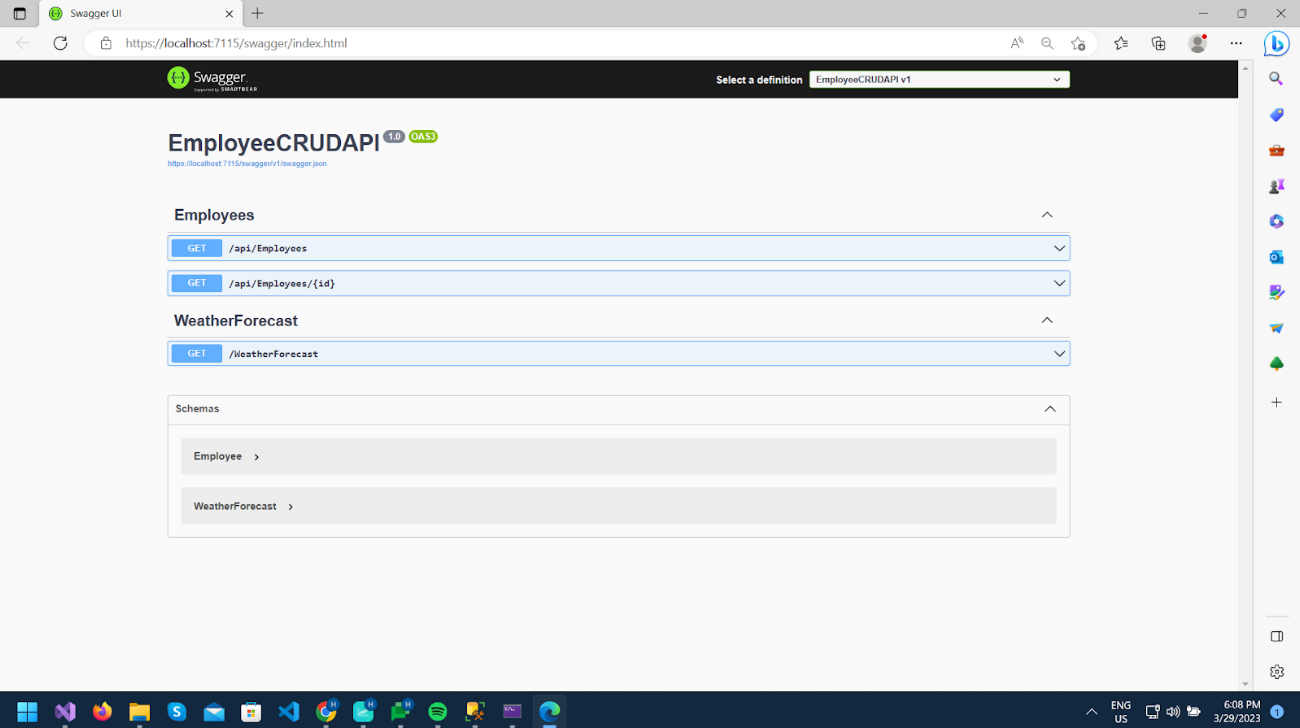
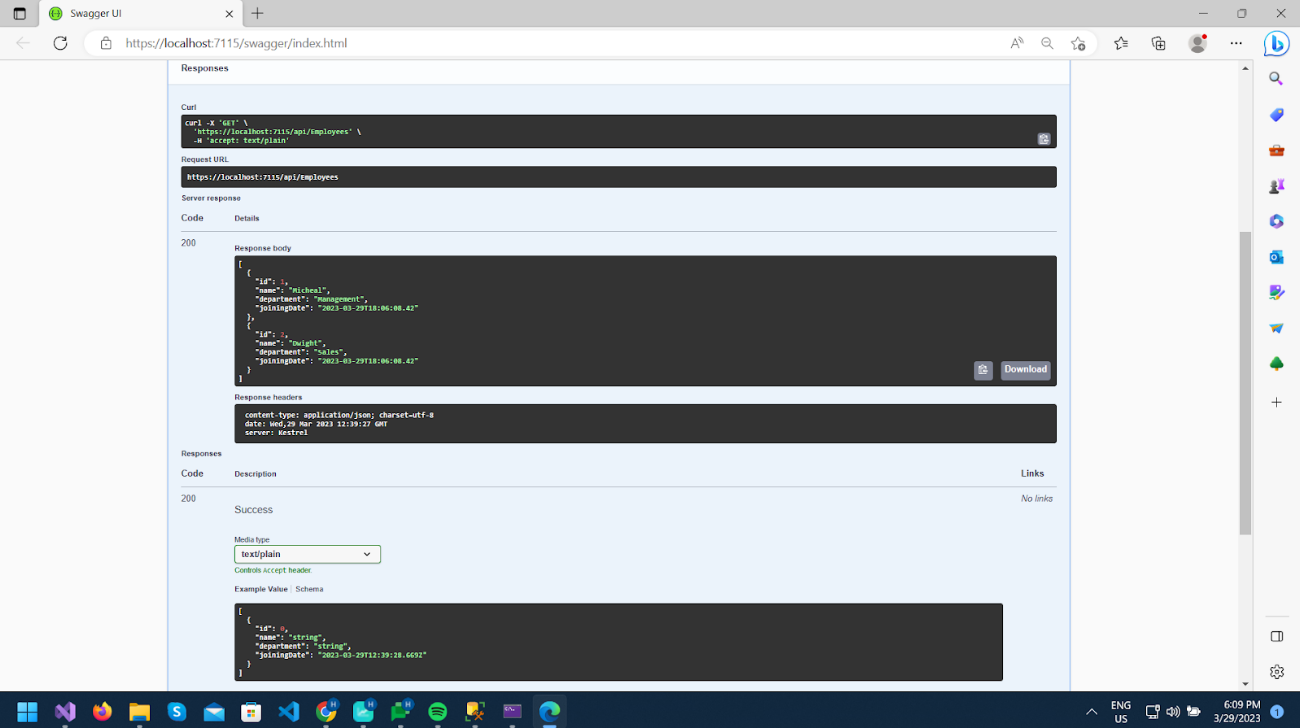
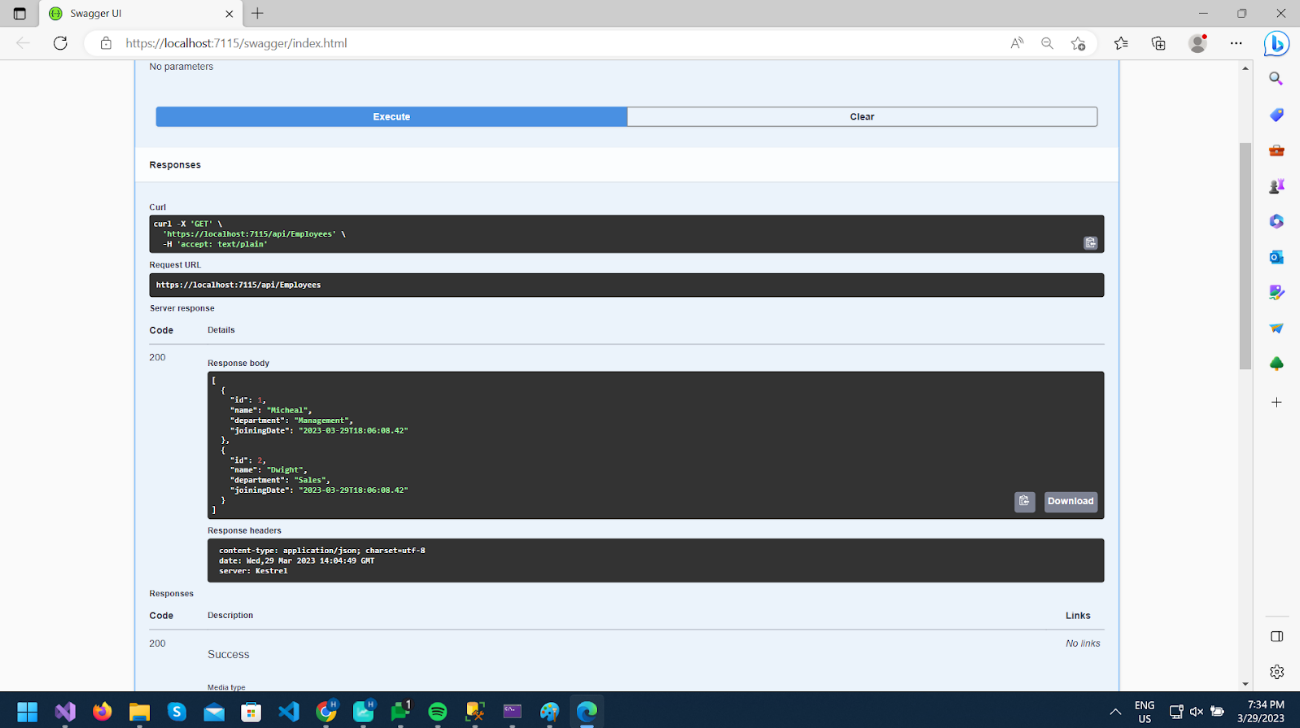
The first method calls https://localhost:7115/api/Employees and gives a list of both records, as you can see in the image.
In the following method, pass the id as 2, and it will call url https://localhost:7115/api/Employees/2 and give data of record with id 2.

Now add a HttpPost method PostEmplyee to create new records as per below.
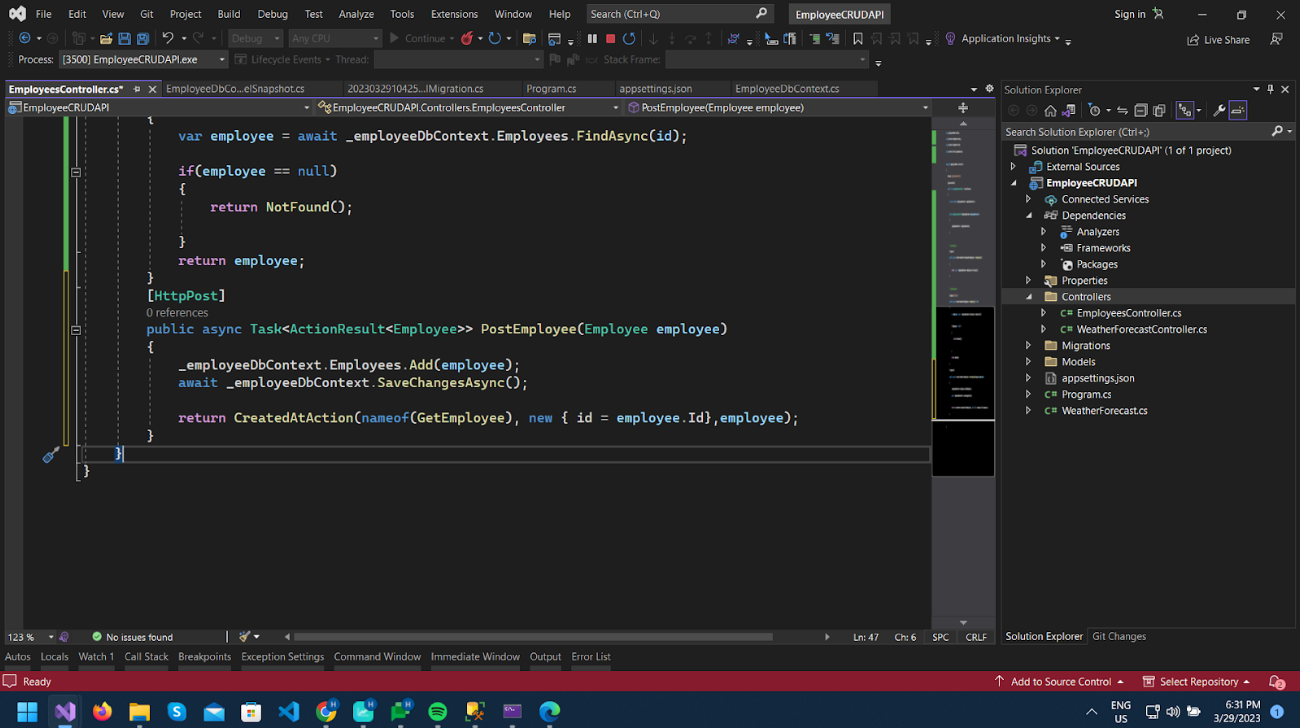
We have added a parameter of type Employee class which we will pass in the Body of POST request to add to the Employee table.
Also, we are returning the CreatedAtAction method, which will return HTTP Status 201 and will add a Location header in the response with url to get that new record we added.
Now run the project, and provide the necessary employee information as specified below. Execute the POST method, and check the result.
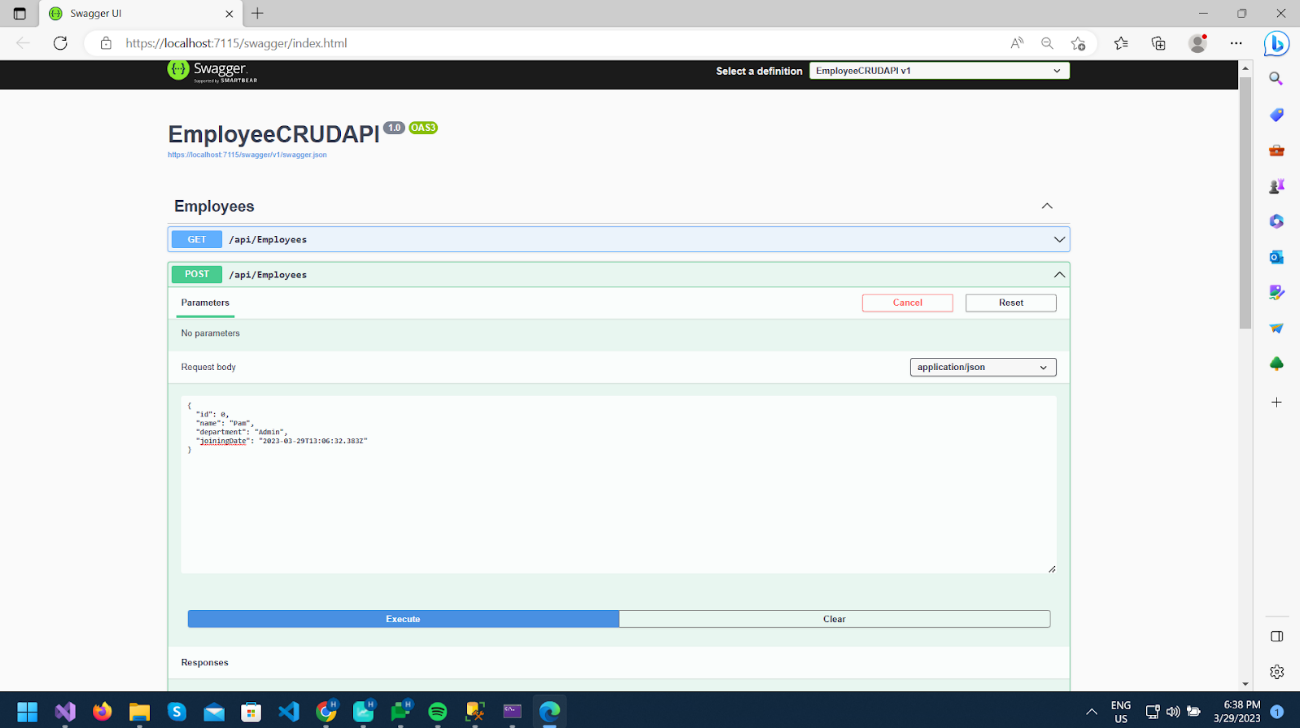
In response, we get a 201 Status code; in the location response header, we get a url to get a newly added employee.
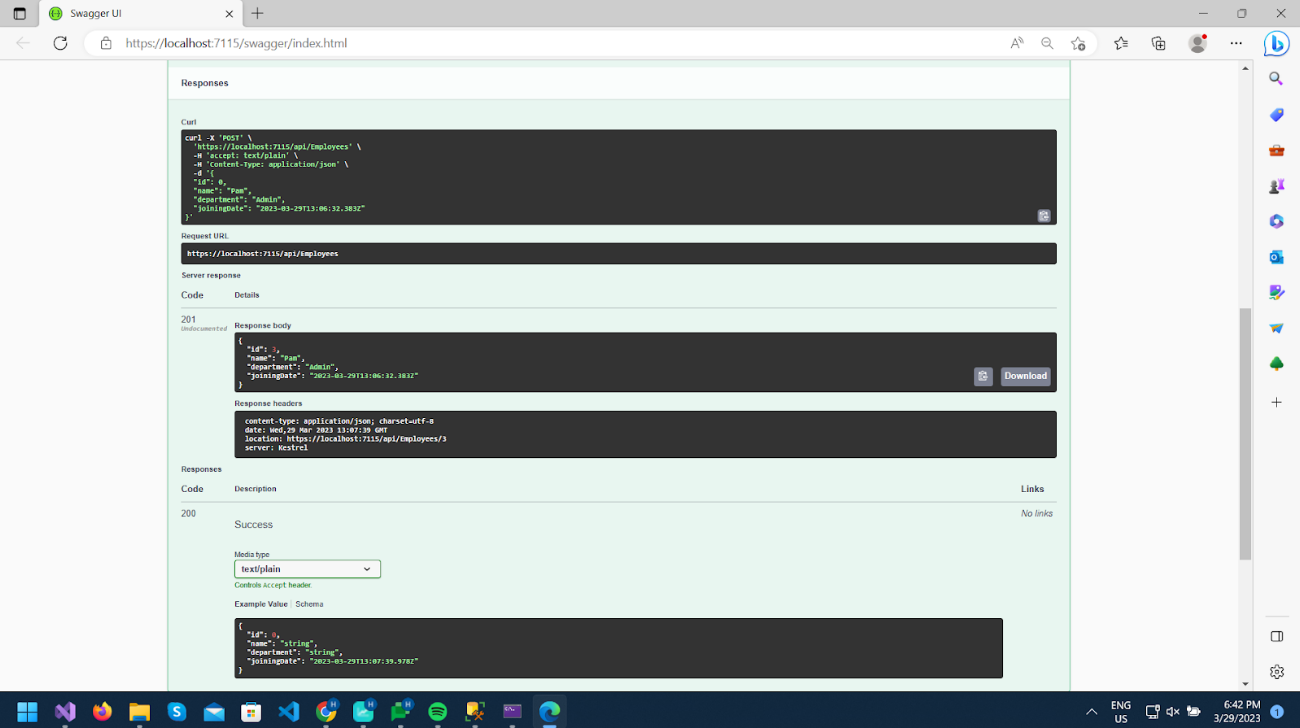
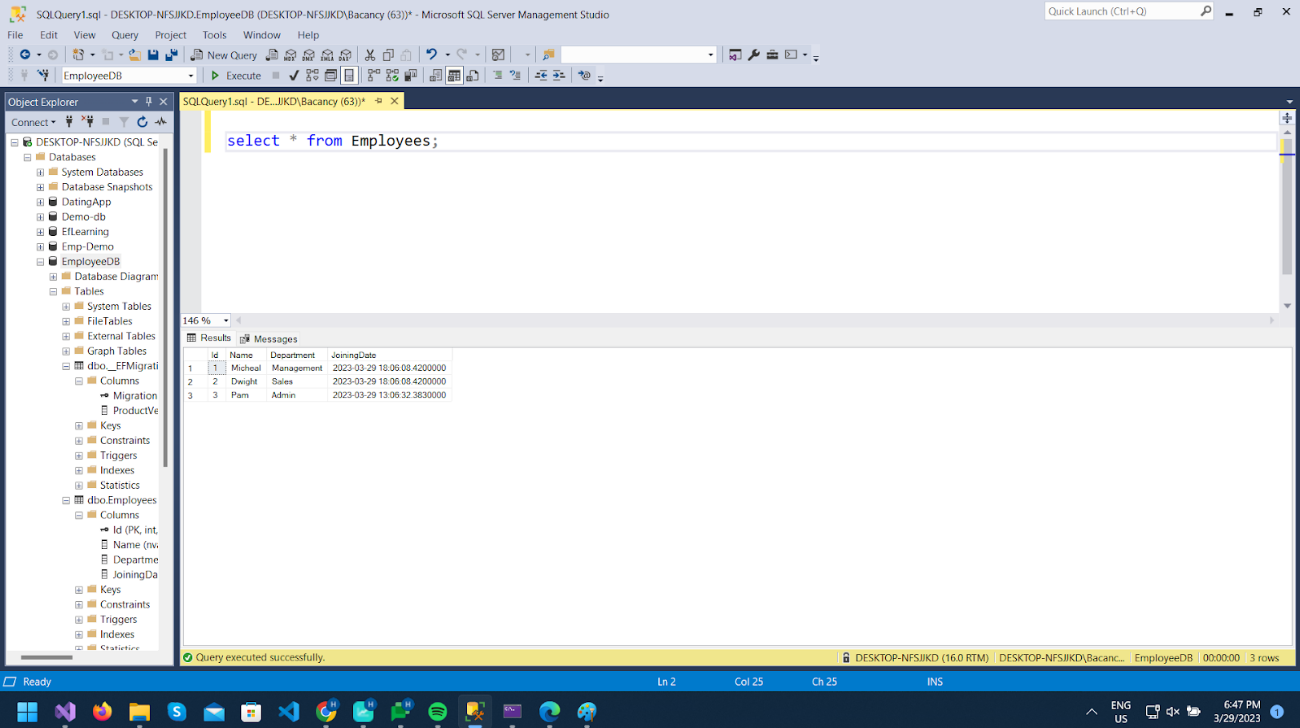
And you can check new records in the database table.
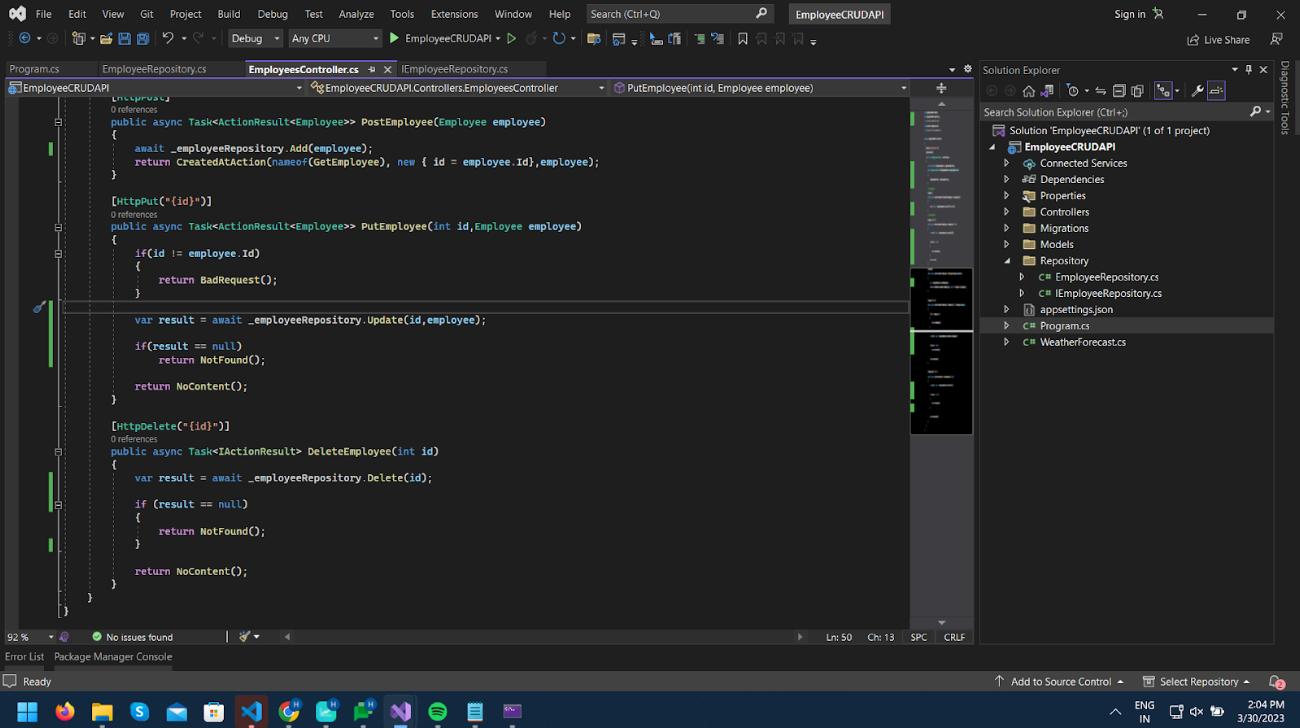
We will add the HttpPut method PutEmployee to Update the specific employee by id.
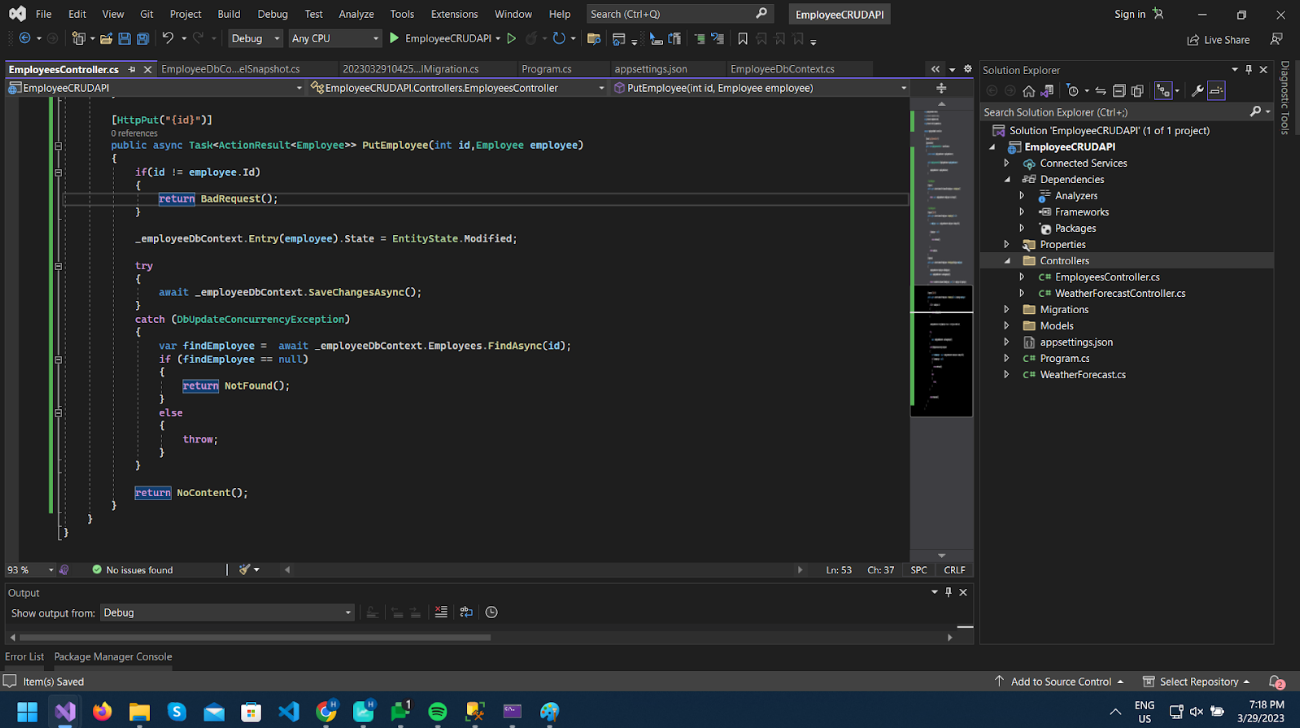
Here we will pass the id in Url and then pass the Employee object in the request body same as the previous POST method.
Response from the PUT method will be 204 (No Content) if the operation is successful.
Now let’s test API by updating some data. Here I am updating the “Department” property to “Sales” from “Admin” for id 3.
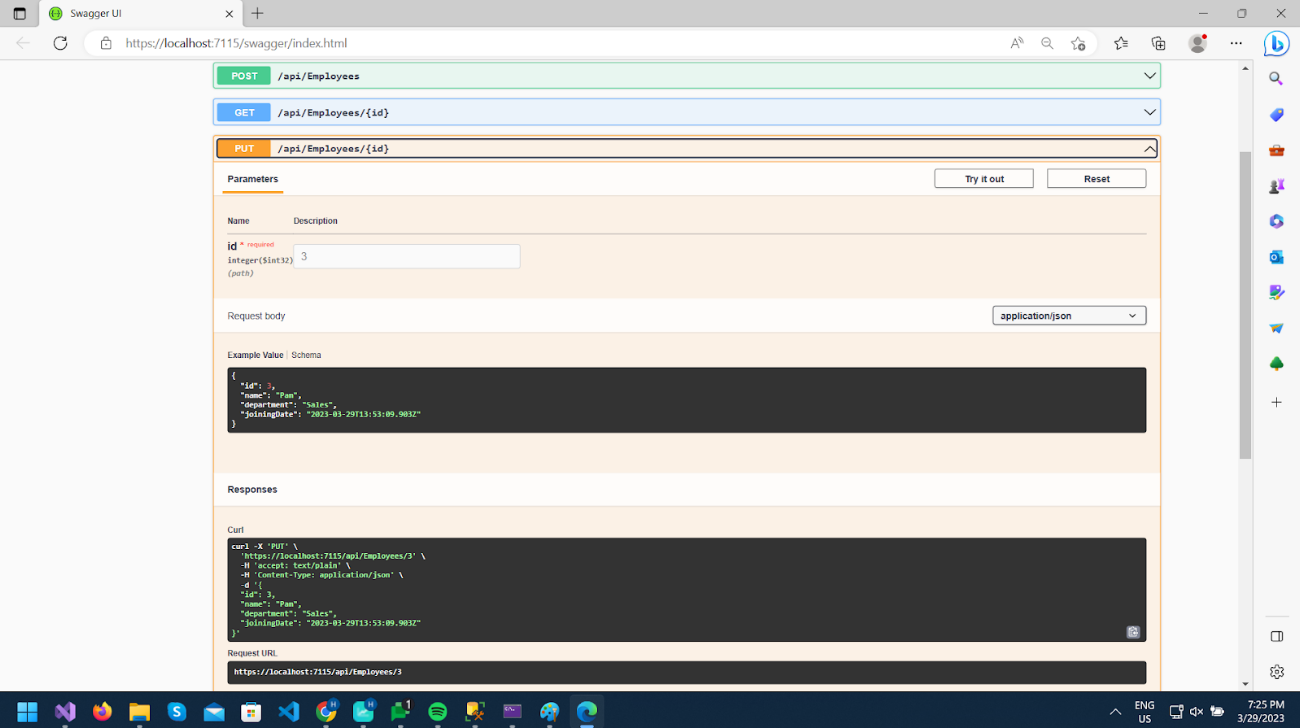
As we can see Response status is 204.
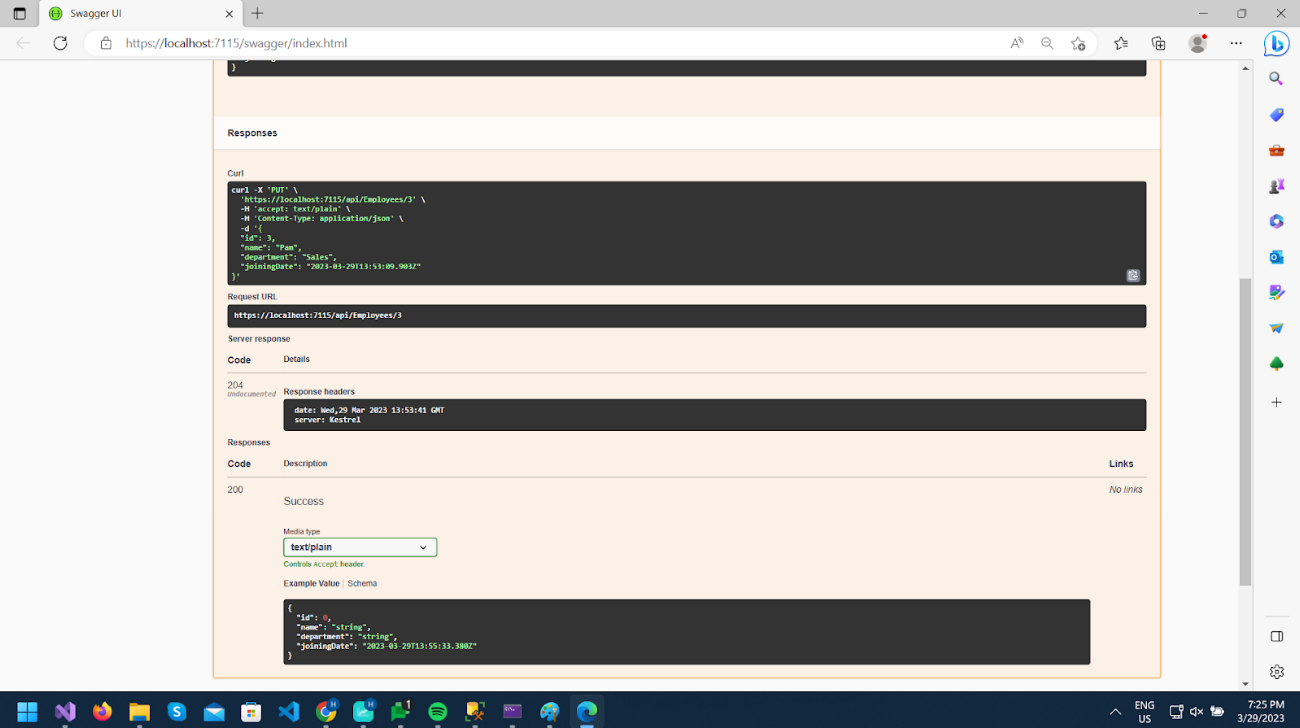
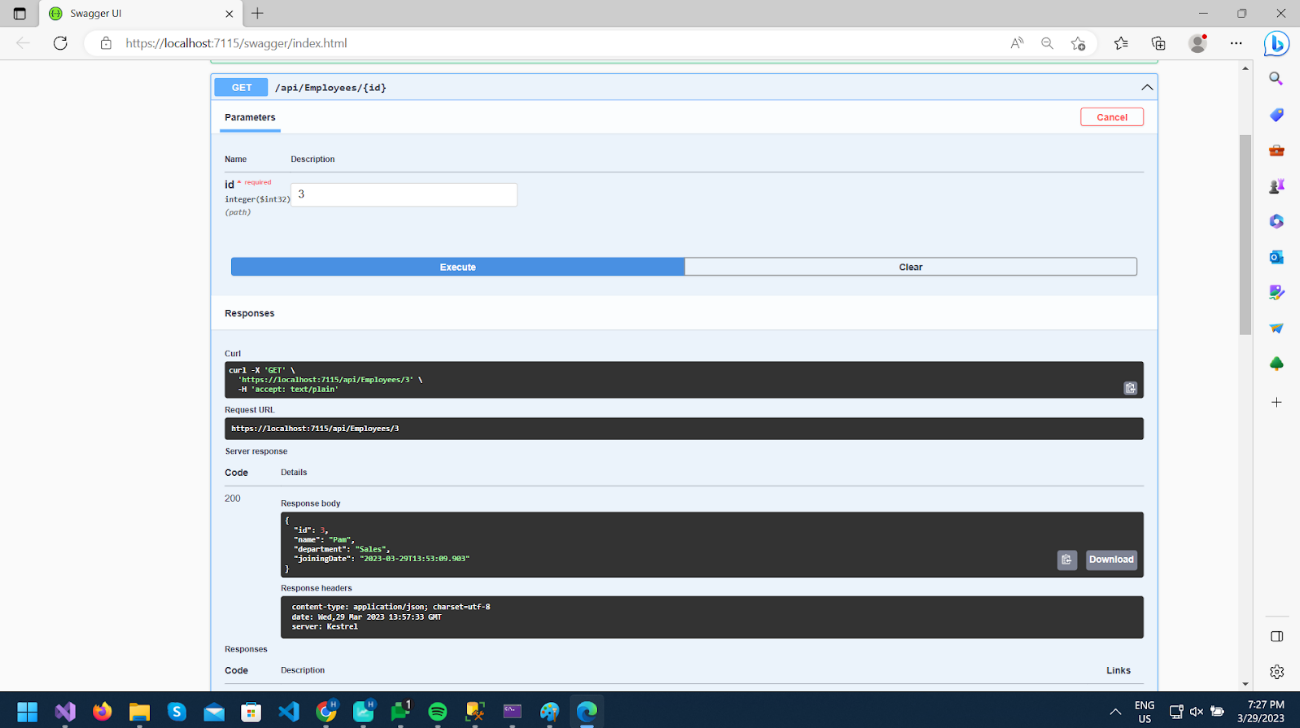
You can call GET /api/Employees/3 and check updated data.
Now let’s create the HttpDelete method DeleteEmployee as per below.
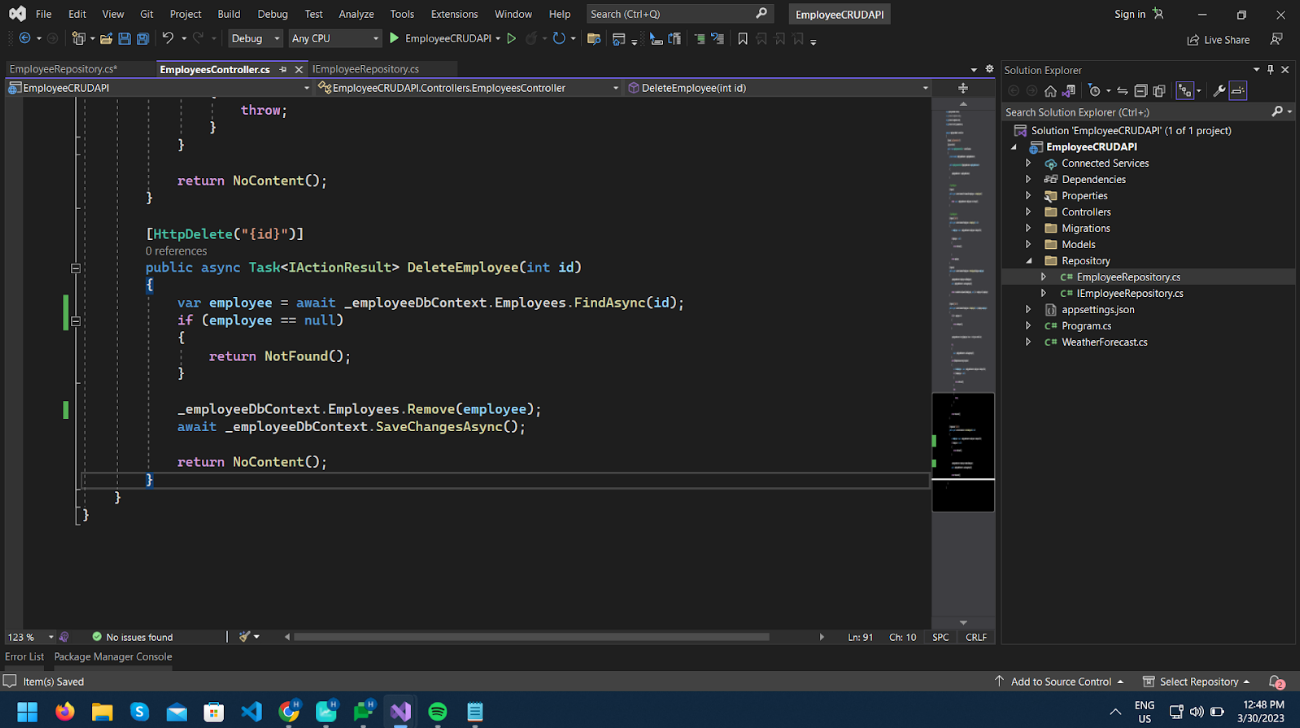
It will also return status 204 (No Content) if the operation is successful.
Let’s run the project and test the code.
Here I am passing the id as 3.
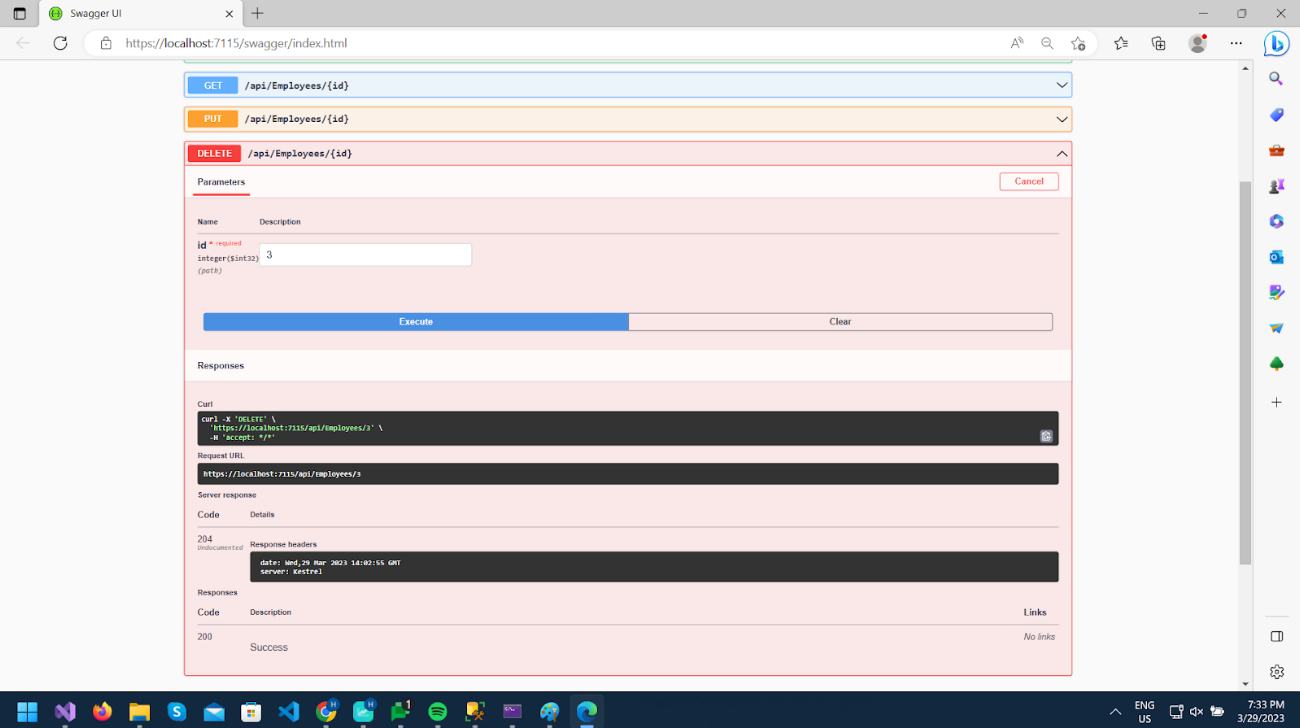
As we can see Response status is 204.
You can call GET /api/Employees and see that the record is deleted of id 3.
Next, we will add Repository Pattern to our project.
Repository Pattern serves as a middle layer between Application and Data Access Logic. It provides an abstraction for Data Access Logic. Instead of directly calling DbContext methods of Employees in Controller, Here we create a Repository class for the Employee entity. The Repository class encapsulates the data access logic, allowing for better separation of concerns. In this tutorial we will then inject the Repository class into the Controller, enabling the Controller to interact with the data through the Repository.
Now we will Implement this in our application,
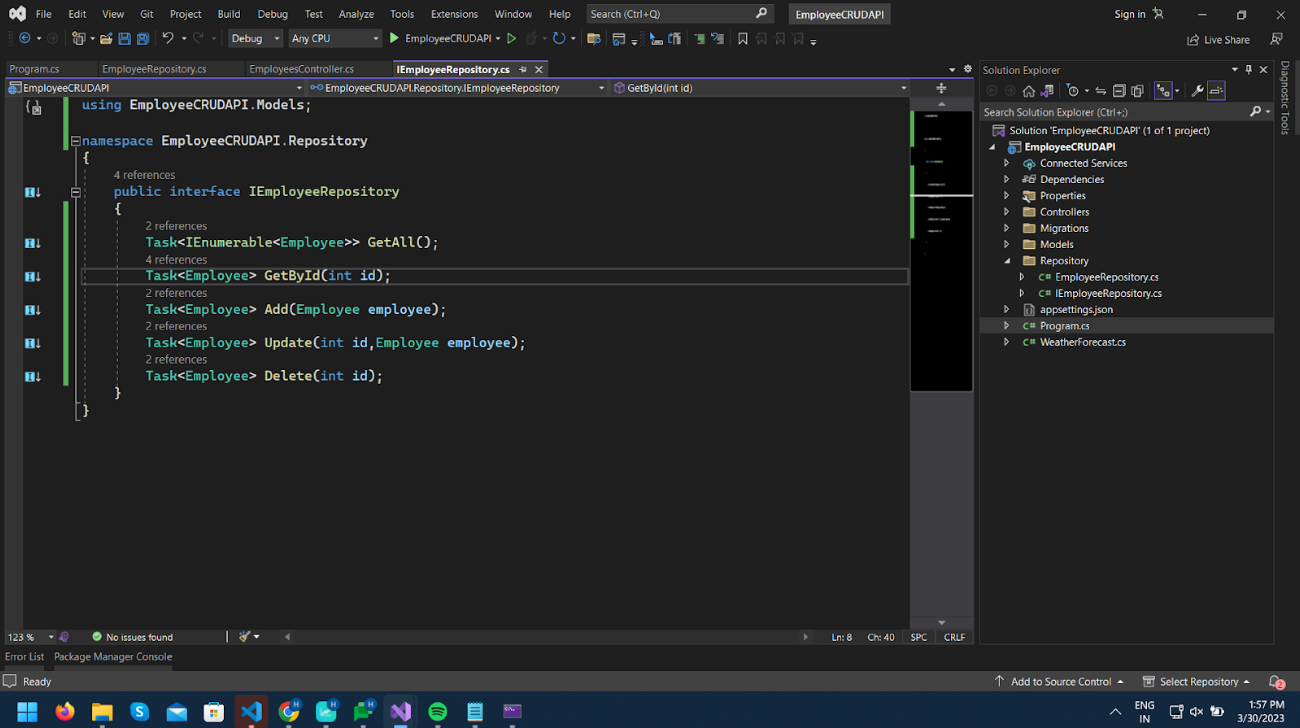
Create a new folder called Repository in Project and add IEmployeeRepository.cs Interface and EmployeeRepository.cs class in Repository Folder.
In IEmployeeRepository.cs, declare all the methods below for CRUD operation.
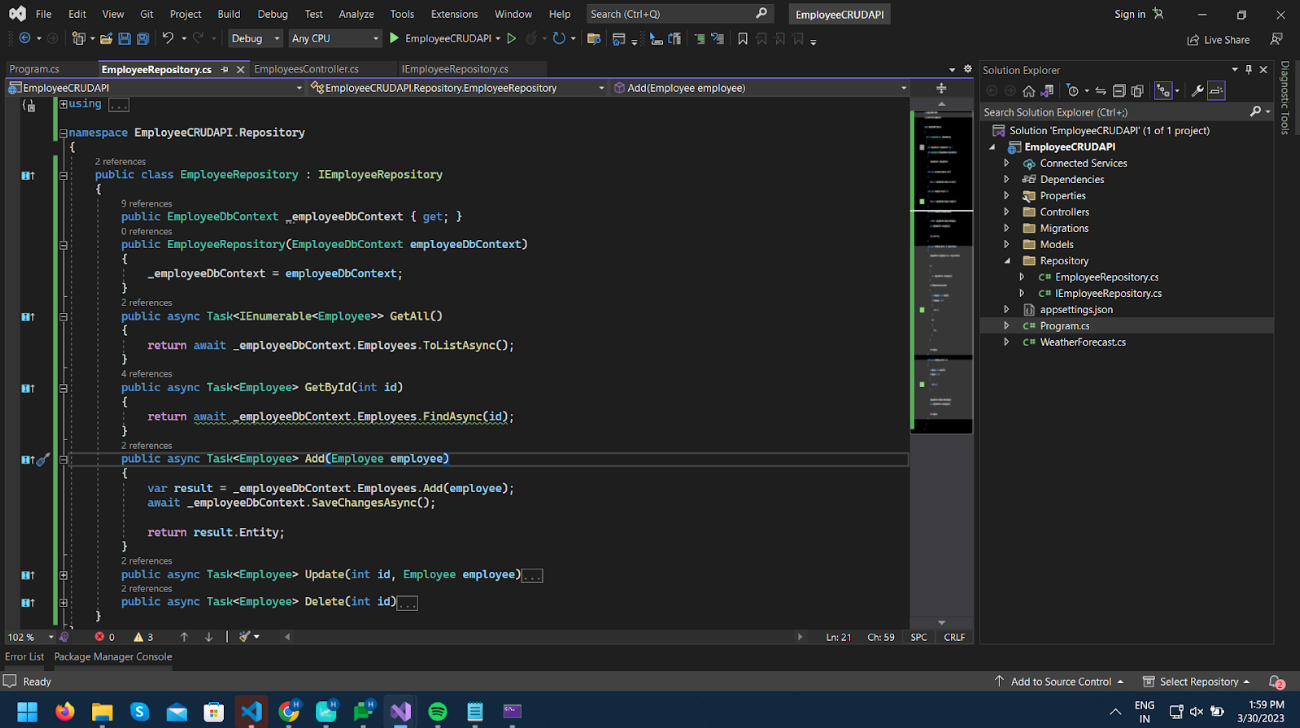
In EmployeeRepository.cs implement Interface, inject EmployeeDbContext and add logic as we wrote in Controller.
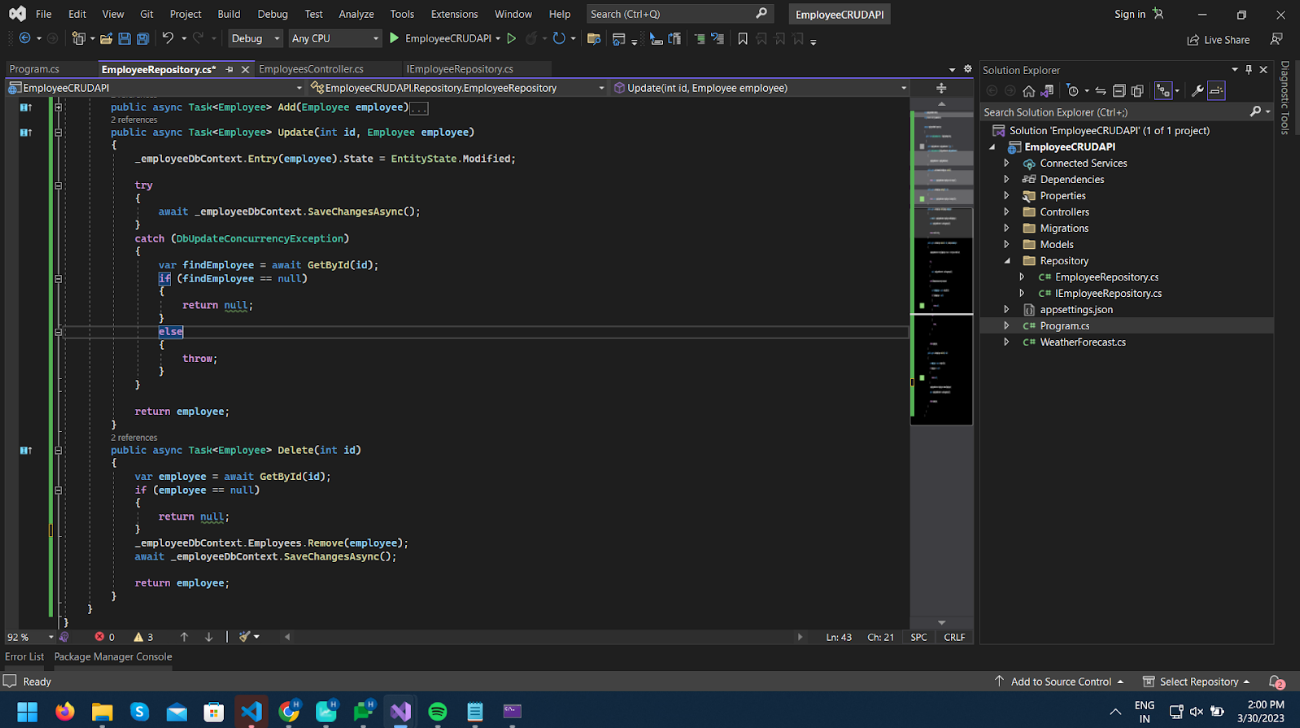
Register the EmployeeRepository service,
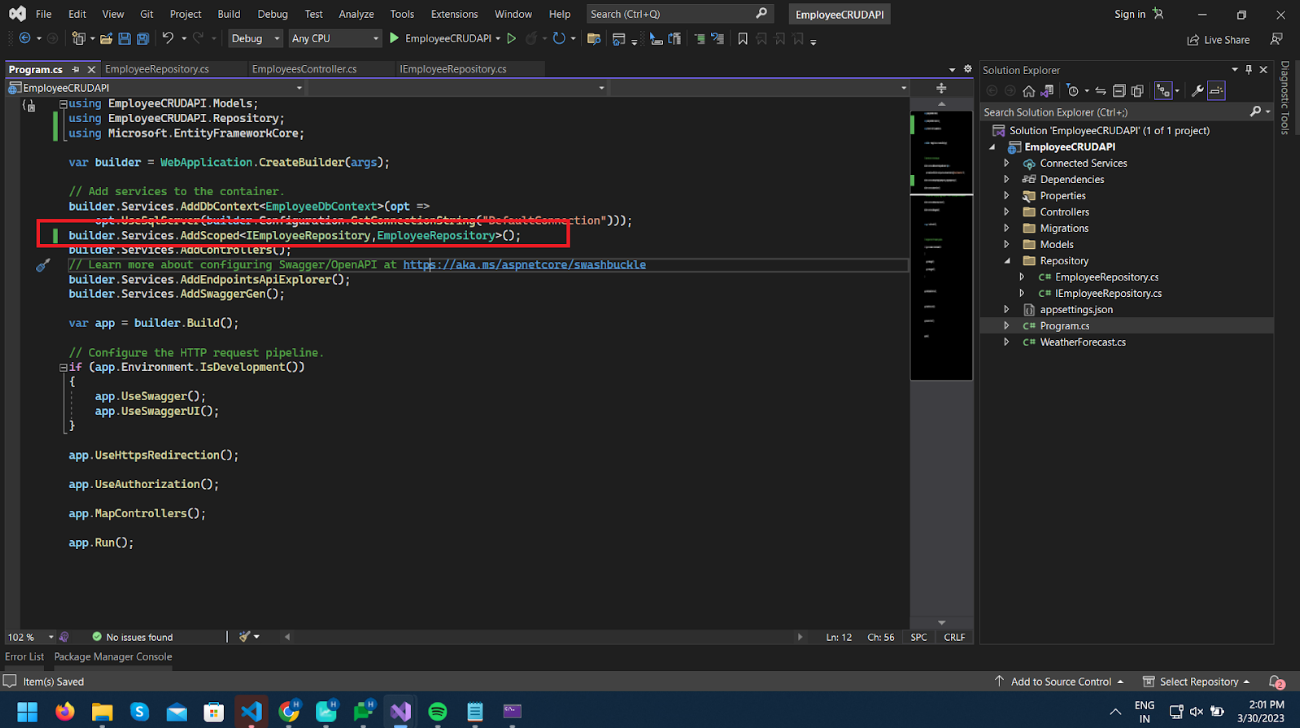
Inject this service into Controller, and modify logic by removing EmployeeDbContext and using EmployeeRepository class.
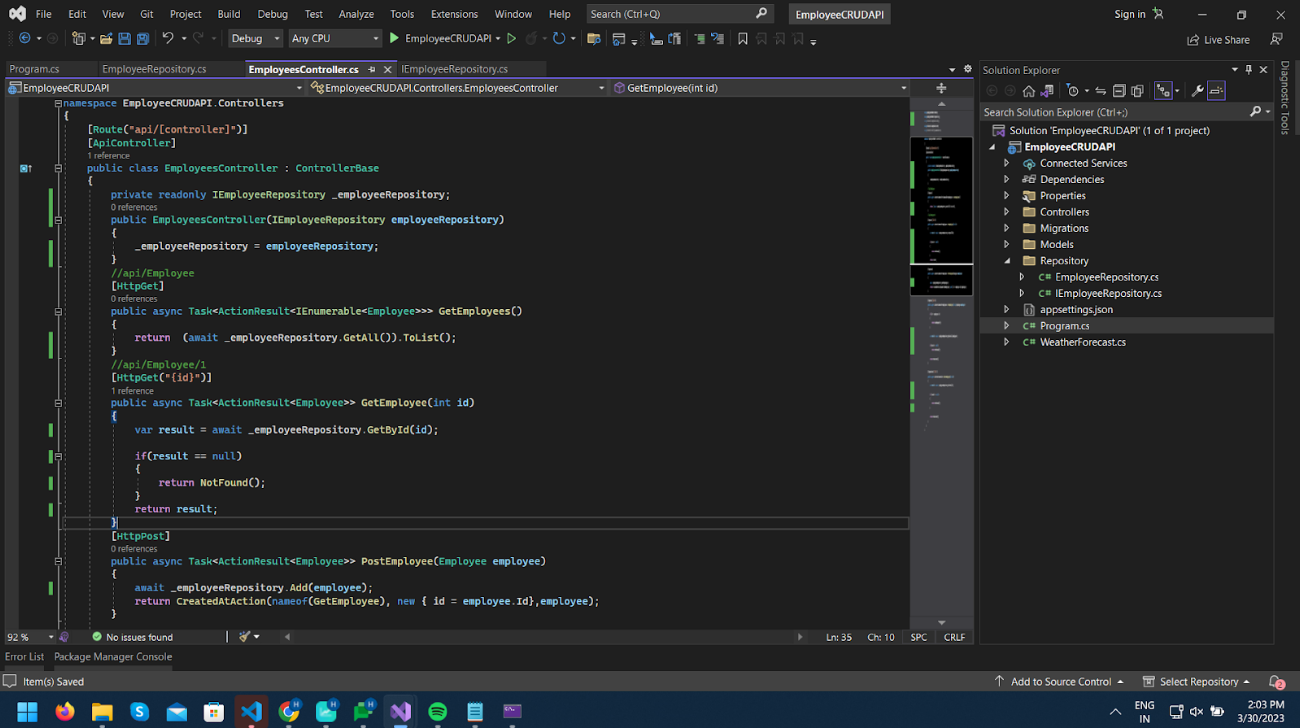
You can run and test the project; it should work as before.
When you want to add a new Entity like Department, you must follow the same step we did for Employees to create a Repository. You can also create a Generic Repository interface and class for basic CRUD operations. Hire dot NET developer and witness your projects soar to new heights.
Here’s the source code of Web API in the .NET 6 example. Feel free to clone the repository and play around with the code. Start developing your demo application and learn how to build a CRUD operation.
So, this was all about developing Web API using Entity Framework Core in .NET 6. We hope the tutorial helped you build a basic CRUD operation with the Entity framework repository pattern. If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to contact us. For more such tech solutions, check out our other .Net tutorials.
Your Success Is Guaranteed !
We accelerate the release of digital product and guaranteed their success
We Use Slack, Jira & GitHub for Accurate Deployment and Effective Communication.