A decade ago, webpages were displayed as static content; I am talking about a time where the web pages were simply plain, no interaction at all. The organizations were running with a motive to showcase the information of its products as well as the organization to generate sales leads only. The Server-side was the only available option to get your HTML onto a screen. Whereas moving forward to today, server-side rendering is getting more traction, and for that credit goes to the front-end community. Today the server-side solution is not only one available solution; client-side rendering and pre-rendering are also available solutions and indeed a pretty good strategy.
I am writing this blogpost to discuss three main rendering methods; server-side rendering (SSR), client-side rendering (CSR), and pre-rendering.
You may also like: React.js for Efficient Server Rendering, Using Node.js as a Proxy Server
What is Client-side Rendering?
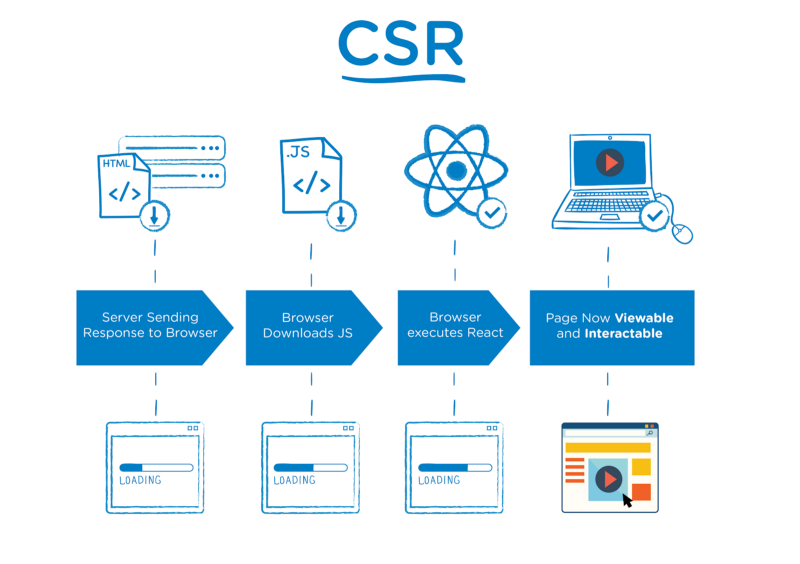
With client-side rendering, you can make the entire website rendered in the browser with JavaScript, and your first request loads the page layout, CSS, and JavaScript.
In this procedure, connection with the server happens only for getting the run-time data. It is not required to reload the UI after every call to the server. The client-side framework contrives to update UI with changed data by re-rendering only that particular DOM component.
Single Page Applications only fetch data from a RESTful API that provides data to the client and then displays that data.
Client-side includes productive, animated interactions and transitions or fade a dialog into view. It can be hosted via a content delivery system to improve performance as well as scalability by removing the load from your server. You can easily create automated deployments by using services like Surge and Netlify.
What is SSR- Server Side Rendering?
You may also like, How to Do Server-side Rendering With the Help of Vue and Nuxt.js?
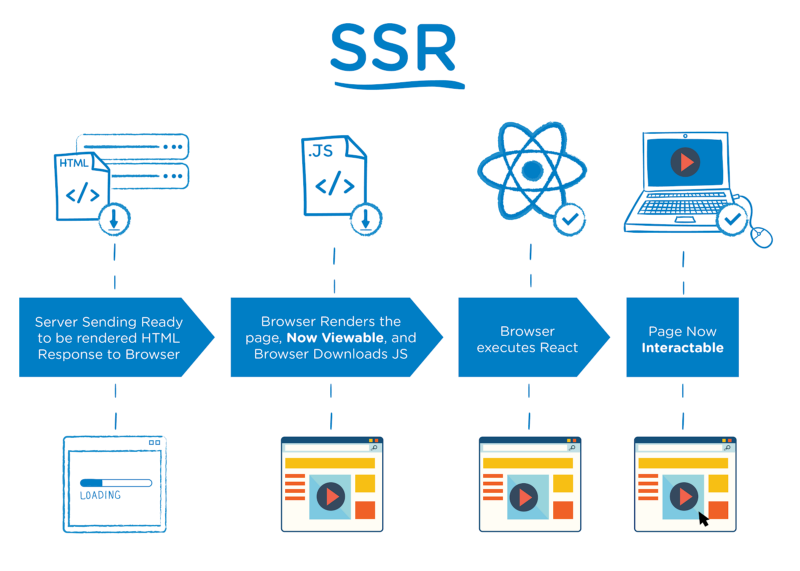
In server-side rendering, when a user creates a request to a webpage, the server equips an HTML page by eliciting user-specific data and sends it to the user’s machine over the internet.
After completing this process, the browser then interprets the content and displays the page. This entire method of fetching data from the database, creating an HTML page, and sending it to the client happens in mere milliseconds.
If your content is crawlable via server-side rendering by search engines, then your site and pages will appear in Google search results, and a preview will show up with the page title, description, and image. SSR is one of the conventional ways of rendering web pages on the web browser.
What is Pre-rendering?
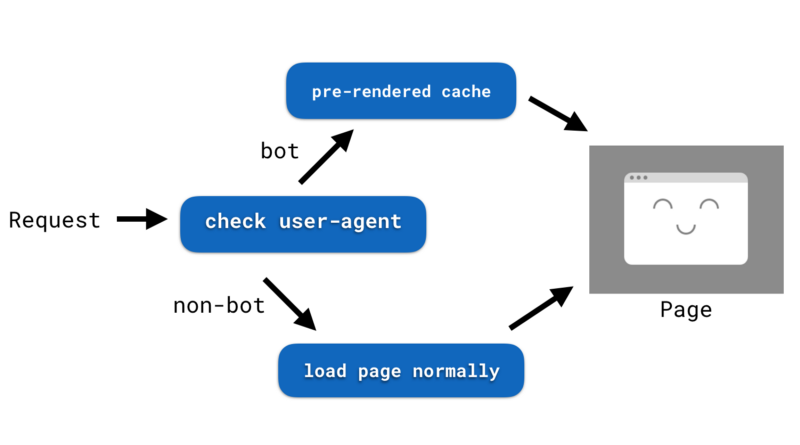
Pre-rendering is a tradeoff between client-side rendering and server-side rendering and a process of loading a webpage ahead of time, waiting for it to finish rendering, and then reversing the resulting HTML and JavaScript as a result to the requesting entity.
Once the page is fetched, internal routing is done dynamically to take benefit of a client-side rendered website as well as the pre-rendered page displays a template when the data waits to be rehydrated with AJAX/XHR requests.
When you design the architecture of a page that is shown before the final content is rendered to the screen, a static snapshot of the page is immediately taken that can be useful to represent the content to search engines on page load without providing anything.
Pre-rendering is a solution where you send bots of the rendered version of the DOM, which is the most crucial element that makes sure the search engines are being served a legitimate, authentic representation of the JavaScript-based equivalent at all times.
Search engines can execute JavaScript when your web page depends on some data to expand the content of the page; that’s where you run into problems.
When to use?
Client-side rendering
- You can use CSR if your application has a complex UI with fewer features.
- Available data is large and dynamic.
- Read preference of the site is less than write preference.
- The focus is on rich sites with a large number of users.
Server-side rendering
- You can choose SSR if the model of your graphic is complex and computationally intensive.
- Available data can be small or large.
- Write and read preference of the site is comparatively equal.
- The focus is on rich sites with only a few users.
Pre-rendering
- Adopt pre-rendering if your application has a simple UI with fewer features.
- Available data is less and dynamic.
- Write preference of the site is less than reading preference.
- The focus is on rich sites.
Final Thoughts
In this blog about rendering, you can quickly know how to create dynamic content for the web and the fundamentals of when you should consider using CSR, SSR, and pre-rendering. If you are using any kind of front end technology like Angular, Vue.js, or React and want to implement SSR, then kindly get in touch with us as we are experts at implementing SSR in your front-end web application.
Hopefully, you have a better understanding of what is client-side rendering, server-side rendering, and pre-rendering and, most importantly, when to use them as the mechanisms differ from each other. The three types of rendering have valid use-cases and make sure you study each of them and that you gather enough information about the project to be developed to make a conscious decision before starting development.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Which is faster client-side rendering or server-side rendering?
Generally, a client machine has a lot of spare computational power that is not used rather than the server can run requests for thousands of users. If you look at the client machine, it is not powerful compared to the server as a server manages the code much faster than scripting. Hence, you can say that the server-side is faster compared to the client-side.
-
Is server-side rendering better?
Yes. Server-side rendering is better because the factors like sending initial requests and performance are a bit faster than client-side rendering and pre-rendering. It is simple and does not require round trips to the server.
-
Is JavaScript client-side or server-side?
JavaScript is a Client-side language that is executed at the user-side, whereas PHP is a server-side scripting language because it gets executed at the server-side.


