Summary
Full-stack development has gained significant traction in the market due to the immense benefits it offers like streamlined processes, scalability, and adaptability to the dynamic demands of the ever-evolving business and tech landscape. This blog post focuses on crucial aspects of full-stack development with Swift and Vapor, covering both backend (server-side) and front-end (client-side) components. Let’s dive further to explore a high-level overview of the steps to create a full-stack app with Swift and Vapor.
Table of Contents
Introduction To Full Stack Development With Swift And Vapor
Full stack development with Swift and Vapor offers a comprehensive and streamlined approach to creating web applications. Swift (Apple’s powerful and intuitive programming language) known for its ease of use and performance, does wonders and becomes even more powerful when combined with Vapor, a server-side Swift web framework. This deadly combination enables developers to leverage the language’s versatility to build front-end and back-end components of your application.
Backend (Server-side) with Vapor
The initial step involves prerequisites to be fulfilled before moving ahead. Follow the steps below,
Prerequisites
1. Install Vapor: Use the following commands to install the Vapor Toolbox.

/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install.sh)" brew tap vapor/tap brew install vapor
2. Create a New Vapor Project: Open Terminal and run the following commands to create a new Vapor project.
Project Structure
1. The project structure generated by Vapor will include directories like Sources, Public, and Resources.
2. ‘Sources/App’ contains your server-side Swift code in files like ‘routes.swift’.
Define API Routes
1. Edit the ‘routes.swift’ file to define your API routes and handlers. For example,

import Vapor
func routes(_ app: Application) throws {
app.get { req in
return "Hello, world!"
}
app.get("api", "example") { req -> String in
return "This is an example API endpoint."
}
}
Run The Server
- Execute ‘vapor run’.
- Once built successfully, your local server will be ready.
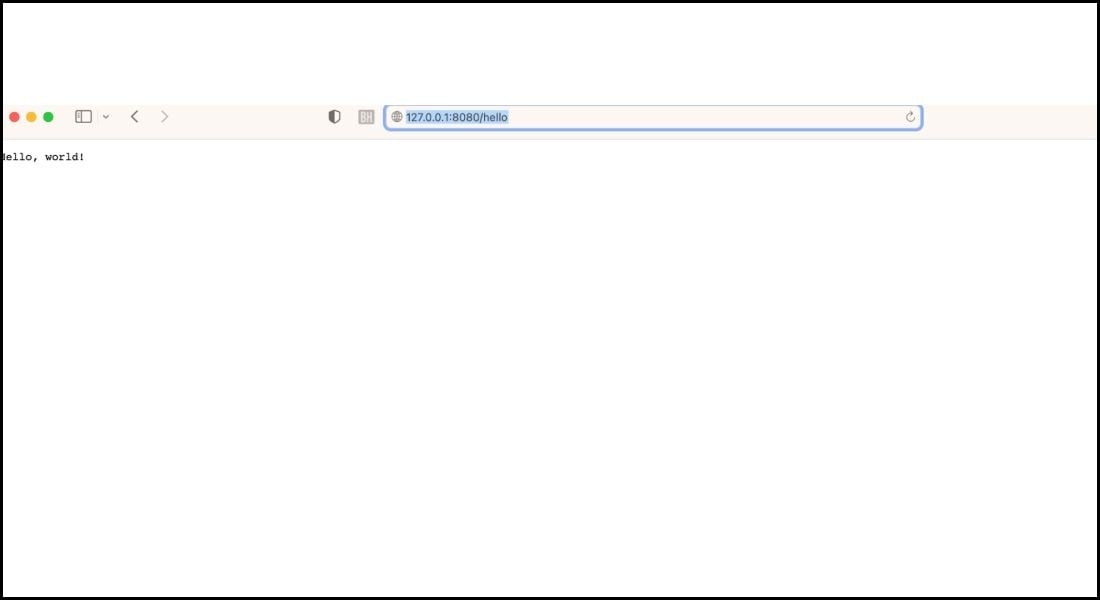
- Visit ‘http://127.0.0.1:8080’ in your browser to test your Vapor server.
- ‘Hello World,’ you will get a response like the below image:
Creating a Query String Route
- Open ‘Routes.swift’ in the Sources/App folder.
- Now, create a new route that accepts a query parameter.
- Replace the existing content with the following code:

import Vapor
func routes(_ app: Application) throws {
// Handle GET requests to /search
app.get("search") { req -> String in
// Access the "query" parameter from the query string
if let query = req.query["query"] {
return "Search query: \(query)"
} else {
return "No search query provided"
}
}
}
In this example, the route “/search” accepts a query parameter named “query.” We retrieve the value of the query parameter using req.query[“query”]. If the parameter is present, we return a message with the search query; otherwise, we indicate that no search query was provided.
Handling query strings in Swift on the server with Vapor is fundamental to building dynamic web applications. You can use query parameters to make your routes more flexible and responsive to user input. This simple example serves as a starting point for incorporating query strings into your Vapor projects, and you can build upon it to create more complex and feature-rich applications.
Creating Route Groups
- Open ‘Routes.swift’ in the ‘Sources/App’ folder.
- We’ll create a simple example with two route groups for authentication and user-related actions. Replace the existing content with the following code:

import Vapor
func routes(_ app: Application) throws {
// MARK: - Authentication Routes Group
let authGroup = app.group("auth") { authGroup in
authGroup.get("login") { req in
return "Login Page"
}
authGroup.get("register") { req in
return "Registration Page"
}
}
// MARK: - User Routes Group
let userGroup = app.group("user") { userGroup in
userGroup.get("profile") { req in
return "User Profile Page"
}
userGroup.get("settings") { req in
return "User Settings Page"
}
}
}
In this example, we’ve created two route groups: ‘authGroup’ for authentication-related routes and ‘userGroup’ for user-related routes. Each group contains a couple of sample routes.
Notice how we use the ‘app.group’ method to create these groups.
Leveraging route groups in Swift server-side applications with Vapor is a powerful way to enhance code organization and maintainability. Whether you’re working on authentication, user-related functionalities, or any other application part, it provides a clean and modular approach. As your application grows, embracing this organizational strategy creates a more scalable and maintainable codebase.
MVC Pattern and Controllers
Model
The model represents the application’s data and business logic. It encapsulates the information and behavior of the application, ensuring data consistency and integrity. In Swift, models are often defined as structs or classes.
View
The view is responsible for presenting the data and capturing user input. In server-side development, templates that generate HTML or other response formats often represent views.
Controller
The controller acts as an intermediary between the model and the view. It processes user input, updates the model, and triggers the appropriate view to reflect the changes. Classes typically represent controllers in Swift.
Hire Full Stack Developers and Join The Ranks With Leading Enterprises.
Creating a Swift Server-Side Application with MVC
Let’s create a simple Swift server-side application that follows the MVC pattern using Vapor. We will focus on the controller aspect of the MVC pattern.
Step 1: Set Up a Vapor Project
Create a new Vapor project using the following commands:
Open the Xcode project (‘MVCApp.xcodeproj’) that Vapor has generated for you.
Step 2: Create a Controller
- Create a new Swift file called ‘MyController.swift’ in the ‘Sources/App/Controllers’ Directory.
- Define a simple controller with a sample method:

import Vapor
final class MyController {
func welcomeHandler(req: Request) throws -> String {
return "Welcome to the MVC App!"
}
}
Step 3: Register the Controller's Route
Open ‘Routes.swift’ in the ‘Sources/App’ directory. Register the controller’s route in the ‘routes’ function:

import Vapor
func routes(_ app: Application) throws {
let myController = MyController()
// Register the route handled by the controller's method
app.get("welcome", use: myController.welcomeHandler)
}
Understanding Middleware in Swift
Middleware functions are executed in the order they are added to the application. They can intercept incoming requests before they reach your route handlers, or modify the outgoing responses before they are sent back to the client.
Middleware can be used for various purposes, including
- Authentication: Verify user credentials before allowing access to certain routes.
- Logging: Log information about incoming requests and outgoing responses.
- Error Handling: Intercept errors and handle them gracefully.
- Request Modification: Modify the request object before it reaches route handlers.
- Response Modification: Modify the response object before it is returned to the client.
Creating a Swift Server-Side Application with Middleware
Let’s create a simple Swift server-side application using Vapor and explore how middleware can be applied.
Step 1: Create a Middleware
- Create a new Swift file ‘LoggingMiddleware.swift’ in the ‘Sources/App/Middleware’ directory.
- Define a middleware class that logs information about incoming requests:

import Vapor
final class LoggingMiddleware: Middleware {
func respond(to req: Request, chainingTo next: Responder) -> EventLoopFuture {
// Log information about the incoming request
print("Received request: \(req.description)")
// Continue to the next middleware or route handler
return next.respond(to: req)
}
}
Step 2: Register the Middleware
- Open ‘configure.swift’ in the ‘Sources/App’ directory.
- Register the middleware in the configure function:

import Vapor
// Called before your application initializes.
public func configure(_ app: Application) throws {
// Register the LoggingMiddleware
app.middleware.use(LoggingMiddleware())
// Other configurations...
}
Advantages of Using Middleware
Middleware serves as a software layer that enables diverse apps and services to interact. In the evolving tech development, the technological infrastructure is becoming more complex by the day, and cloud-based middleware plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth interaction of different components. Without middleware, these systems would struggle to function correctly. Several other factors contribute to the benefits of using Middleware within the process are:
Modularity
Middleware allows you to encapsulate and modularize functionality. Each middleware class can focus on a specific task, promoting code organization.
Intercepting Requests and Responses
Middleware provides a way to intercept and modify both incoming requests and outgoing responses. This flexibility enables various use cases, such as authentication and logging.
Global Application Concerns
Middleware functions as a global concern for your application. They can be applied universally or selectively to specific routes, allowing you to enforce global policies.
Middleware is a crucial aspect of Swift server-side development with Vapor, providing a flexible and powerful way to intercept and process HTTP requests and responses. In this blog post, we’ve explored the concept of middleware and demonstrated its use in a simple Vapor application. By incorporating middleware into your projects, you can enhance security, logging, and other aspects of your server-side applications.
Conclusion
This guide covers comprehensive details of the full stack development with Swift and Vapor, blending the simplicity of Swift and the effectiveness of the robust Vapor framework. The combination enables the developers to seamlessly integrate the frontend and backend components for creating flexible and scalable web applications with optimal performance. This enhances efficiency and enables your development team to stay ahead of the competition. So, whether you are an experienced developer or a new developer learning to code, exploring full-stack development with Swift and Vapor promises significant experience in building sophisticated, future-ready applications.
If you are a business owner looking to leverage these within your next web app development project, get in touch with a Full Stack Development Company like Bacancy and get tailored solutions to experience the best-in-class performance and efficiency based on your needs and requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The advantages include code consistency, high performance, safety and security features, a rich ecosystem, and efficient concurrency handling. The unified language and framework streamline the development process, making it more enjoyable and productive.
Vapor utilizes Fluent, an Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) framework for Swift, to handle data storage. You can define your data models, set up the database, and interact with it using Fluent within your Vapor application.
Vapor is a server-side Swift web framework. It simplifies backend development by providing tools for routing, handling HTTP requests and responses, and integrating with databases. It enhances Swift’s capabilities for building scalable and performant web applications.
Yes, SwiftUI can be employed for front-end development with Swift and Vapor. It allows developers to create a modern, interactive user interface seamlessly integrated with the backend logic.
Your Success Is Guaranteed !
We accelerate the release of digital product and guaranteed their success
We Use Slack, Jira & GitHub for Accurate Deployment and Effective Communication.






